Mouth infections, ranging from toothaches to gum disease, are common concerns that affect individuals of all ages. These infections can be painful and lead to more severe complications if left untreated. Proper mouth infection prevention not only ensures a healthier smile but also prevents long-term oral health issues. By incorporating effective practices into daily life, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these infections.
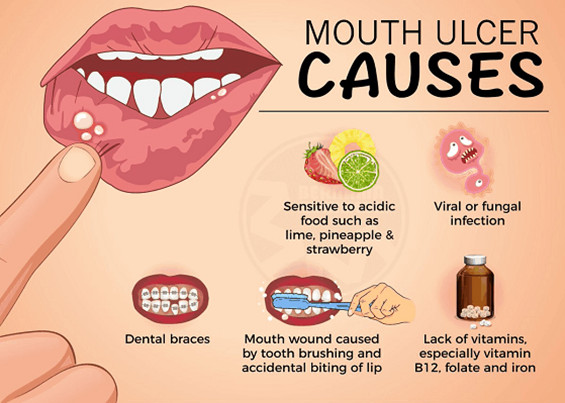
This comprehensive guide delves into the causes of mouth infections, how to prevent them, and the key habits that contribute to optimal oral health. Whether you are looking to avoid gum disease, reduce the risk of mouth ulcers, or prevent tooth infections, the following strategies will help you maintain a clean and healthy mouth.
What Are Mouth Infections?
Mouth infections encompass a wide variety of conditions that affect the tissues within the oral cavity, including teeth, gums, and the tongue. The most common types of mouth infections include:
- Tooth Infections: Often caused by untreated cavities, tooth infections result in painful abscesses and swollen gums.
- Gum Disease: Gingivitis and periodontitis are forms of gum disease that occur due to bacterial buildup along the gum line.
- Mouth Ulcers: These painful sores form inside the mouth and can be triggered by stress, injury, or viral infections.
- Oral Thrush: A fungal infection that leads to white patches on the tongue, cheeks, or roof of the mouth.
While mouth infections vary in severity, they all share common risk factors, such as poor oral hygiene, diet, and smoking. Preventing these infections requires a multi-faceted approach that combines routine oral care with lifestyle changes.
Key Causes of Mouth Infections
Understanding the underlying causes of mouth infections can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent them. The most common causes of mouth infections include:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can allow bacteria to build up on the teeth and gums, leading to cavities, gum disease, and other infections. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates over time and hardens into tartar if not removed regularly. This can cause tooth decay and infections in the surrounding tissues.
2. Dietary Habits
A diet high in sugar and acidic foods can contribute to the development of tooth decay and gum disease. Sugars fuel harmful bacteria in the mouth, which then produce acids that erode tooth enamel and irritate gum tissues.
3. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and chewing tobacco significantly increase the risk of gum disease, mouth ulcers, and oral cancer. Tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums, impairing the body’s ability to fight infections and heal from damage.
4. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or undergoing cancer treatments, are more susceptible to mouth infections. A weakened immune system reduces the body’s ability to fight off harmful bacteria and viruses, making it easier for infections to take hold.
5. Genetics
Genetic predisposition also plays a role in oral health. Some individuals may have a greater tendency to develop gum disease or tooth infections due to inherited factors, such as the strength of their enamel or the composition of their saliva.
Preventing Mouth Infections: Essential Habits for Oral Health
Prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to mouth infections. By adopting effective oral hygiene practices and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce their risk of developing oral infections.
1. Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
Brushing and flossing are the most effective ways to remove food particles, plaque, and bacteria that accumulate in the mouth. The following practices should be incorporated into your daily routine:
- Brush Twice Daily: Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth for two minutes in the morning and before bed. Proper brushing removes food debris and prevents plaque buildup.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque between the teeth and along the gum line, areas that are difficult to reach with a toothbrush.
- Use Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help kill harmful bacteria in the mouth and reduce plaque buildup.
- Replace Your Toothbrush: Change your toothbrush or toothbrush head every 3–4 months to maintain effective cleaning.
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet plays a significant role in maintaining oral health. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals help strengthen teeth and gums, while a reduction in sugary foods can help prevent cavities and gum disease. Key dietary practices include:
- Eat Calcium-Rich Foods: Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals provide calcium, which strengthens tooth enamel.
- Limit Sugar Intake: Reduce your consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, and processed foods, as sugar promotes bacterial growth and acid production in the mouth.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water throughout the day helps wash away food particles and bacteria, maintaining a clean oral environment.
3. Use Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride helps to remineralize tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay. Fluoride toothpaste is an essential part of your daily oral hygiene routine. Additionally, your dentist may recommend professional fluoride treatments for added protection.
4. Avoid Tobacco Products
Avoid smoking and using tobacco products to reduce the risk of developing oral infections, gum disease, and mouth cancer. Tobacco can also cause bad breath and stain teeth, further compromising oral health.
5. Regular Dental Checkups
Regular visits to the dentist are crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing infections. Dentists can detect early signs of tooth decay, gum disease, and other issues that may not be apparent to the patient. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing cannot.
6. Manage Stress
Stress can negatively impact your immune system and increase the risk of developing mouth ulcers and gum disease. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage stress and improve overall health.
7. Protect Your Teeth
Using a mouthguard during sports activities can help prevent dental injuries. If you grind your teeth at night, consider using a nightguard to protect your teeth from excessive wear and tear.
Treatment Options for Mouth Infections
If you do develop a mouth infection despite preventive efforts, early treatment is essential for avoiding complications. The type of treatment depends on the nature and severity of the infection.
1. Antibiotics and Antifungals
In cases of bacterial or fungal infections, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or antifungal medications to eliminate the infection. These medications may be administered topically or orally, depending on the infection.
2. Dental Procedures
For tooth infections or abscesses, a root canal or tooth extraction may be necessary to prevent the infection from spreading. Your dentist will assess the severity of the infection and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
3. Gum Treatments
For gum disease, professional treatments such as scaling and root planing are used to remove plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line. In severe cases, gum surgery may be required to restore gum health.
4. Over-the-Counter Remedies
For mouth ulcers and minor infections, over-the-counter treatments such as topical gels or rinses can provide relief from pain and inflammation. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
Mouth infections are a common but preventable concern that can lead to significant discomfort and health issues if left untreated. By adopting a rigorous oral hygiene routine, making healthier dietary choices, and avoiding tobacco products, you can minimize your risk of developing oral infections. Regular visits to your dentist and early intervention when symptoms arise are key to maintaining optimal oral health. With these proactive steps, you can ensure that your mouth remains healthy, infection-free, and functioning at its best.