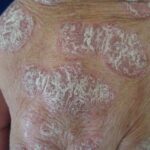
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection caused by the Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a member of the poxvirus family. It leads to small, raised, dome-shaped lesions that are usually painless but highly contagious. This infection commonly affects children, sexually active adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for effective management.
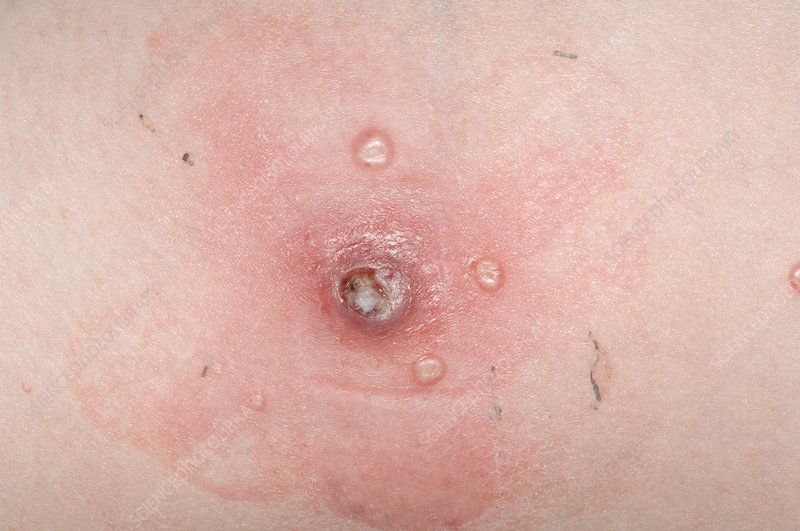
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum spreads through direct skin contact or contaminated objects. The primary causes include:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact – Common in children and sexually active individuals.
- Contaminated objects – Towels, clothing, and sports equipment can harbor the virus.
- Autoinoculation – Scratching or picking at lesions can spread the virus to other parts of the body.
- Weakened immune system – People with compromised immunity, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible.
Symptoms and Identification
Molluscum contagiosum manifests as:
- Small, firm, dome-shaped bumps with a dimple in the center.
- Lesions that are flesh-colored, pink, or white.
- Itching, irritation, or inflammation in some cases.
- Clustering of lesions, especially in areas of skin folds like armpits, groin, and behind the knees.
Risk Factors
Certain groups are more prone to developing molluscum contagiosum, including:
- Children aged 1-10 years.
- Individuals engaging in contact sports.
- Those with atopic dermatitis.
- Immunocompromised individuals (e.g., HIV patients).
Treatment Options
Medical Treatments
- Cryotherapy – Freezing lesions with liquid nitrogen.
- Curettage – Surgical removal using a small blade.
- Topical treatments – Application of podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, or salicylic acid.
- Laser therapy – Effective for stubborn or widespread lesions.
Home Remedies
- Tea tree oil – Has antiviral properties.
- Apple cider vinegar – May help dry out lesions.
- Aloe vera – Soothes itching and irritation.
Prevention Strategies
- Avoid direct contact with infected individuals.
- Maintain good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items.
- Keep skin moisturized to prevent irritation that may facilitate spread.
- Use barrier protection (e.g., condoms) to reduce risk in sexually active individuals.
Molluscum contagiosum is a self-limiting but contagious skin infection. While it often resolves on its own, medical treatment can help speed recovery. Proper hygiene and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of spreading this condition. If lesions persist or cause discomfort, seeking medical advice is essential for effective management.