Musculoskeletal injuries affect the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, and joints. A minor musculoskeletal injury typically includes sprains, strains, and contusions that result from physical activity, accidents, or repetitive motion. While these injuries are not severe, they can cause discomfort and temporary mobility limitations. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment can aid in effective recovery and prevention.
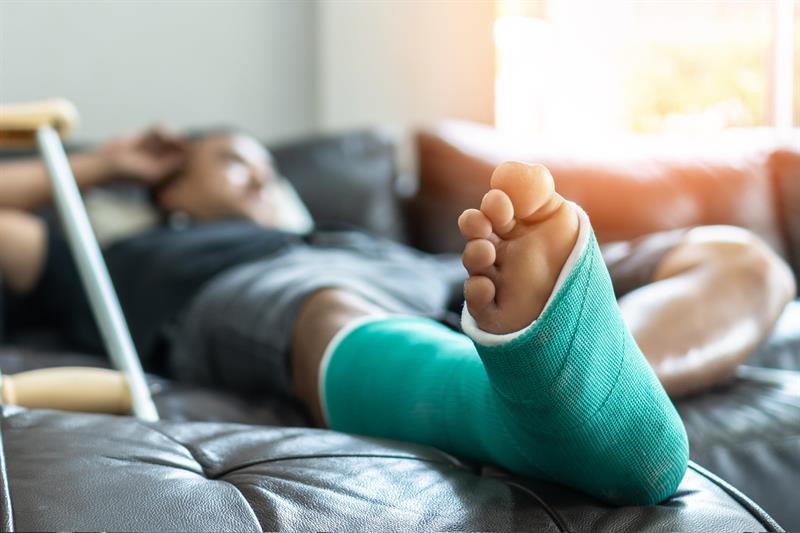

Common Causes of Minor Musculoskeletal Injuries
1. Overuse and Repetitive Motion
- Activities like typing, lifting, or repetitive sports movements can strain muscles and tendons over time.
2. Sudden Impact or Trauma
- A fall, blow, or sudden force can cause sprains, strains, or minor fractures.
3. Poor Posture and Ergonomics
- Improper sitting, standing, or exercising techniques can contribute to musculoskeletal stress.
4. Inadequate Warm-Up and Stretching
- Engaging in physical activity without proper preparation increases the risk of injury.
5. Muscle Fatigue and Weakness
- Weak muscles or fatigue can lead to instability and an increased likelihood of injury.
Symptoms of Minor Musculoskeletal Injuries
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Swelling and inflammation due to tissue damage
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Bruising or discoloration in cases of contusion
- Weakness or instability in the affected joint or muscle
Types of Minor Musculoskeletal Injuries
| Injury Type | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Sprains | Ligament stretching or tearing | Falls, twists, sudden movements |
| Strains | Overstretching of muscles or tendons | Overuse, improper lifting, inadequate warm-up |
| Contusions (Bruises) | Damage to soft tissues from impact | Blunt trauma, falls, direct blows |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation of tendons | Repetitive motion, overuse, poor posture |
Treatment and Recovery Strategies
1. R.I.C.E Method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Rest the affected area to prevent further strain.
- Ice application reduces swelling and pain.
- Compression with bandages provides support and minimizes inflammation.
- Elevation helps reduce fluid buildup and swelling.
2. Pain Management
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen) help manage discomfort.
- Topical anti-inflammatory gels can provide localized relief.
3. Gentle Stretching and Rehabilitation
- Light stretching improves flexibility and circulation.
- Physical therapy may be recommended for gradual strengthening.
4. Supportive Bracing or Taping
- Provides stability and prevents excessive movement that may worsen the injury.
5. Gradual Return to Activity
- Resuming physical activity should be slow and progressive to avoid re-injury.
Prevention of Minor Musculoskeletal Injuries
1. Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down
- Engage in dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching afterward.
2. Strength and Conditioning Exercises
- Building muscle strength reduces stress on joints and ligaments.
3. Maintain Good Posture and Ergonomics
- Use proper body mechanics when lifting or sitting for extended periods.
4. Wear Appropriate Footwear and Gear
- Proper shoes and protective gear can prevent injuries in sports and daily activities.
5. Listen to Your Body
- Avoid overexertion and take breaks when needed to prevent strain and fatigue.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Although minor musculoskeletal injuries usually heal with home treatment, medical attention is necessary if:
- Pain is severe or persists beyond a few days.
- Swelling does not improve with rest and ice.
- The affected limb cannot bear weight.
- There is visible deformity or suspected fracture.
Minor musculoskeletal injuries are common but manageable with proper care and prevention strategies. By following best practices for treatment and recovery, individuals can minimize discomfort and return to normal activity swiftly. If symptoms persist or worsen, professional medical evaluation is recommended to ensure full healing.