Minor bacterial skin infections are common and can occur due to various factors, including cuts, insect bites, and compromised skin barriers. While most cases resolve with minimal treatment, some infections may require medical attention to prevent complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for proper management and prevention.
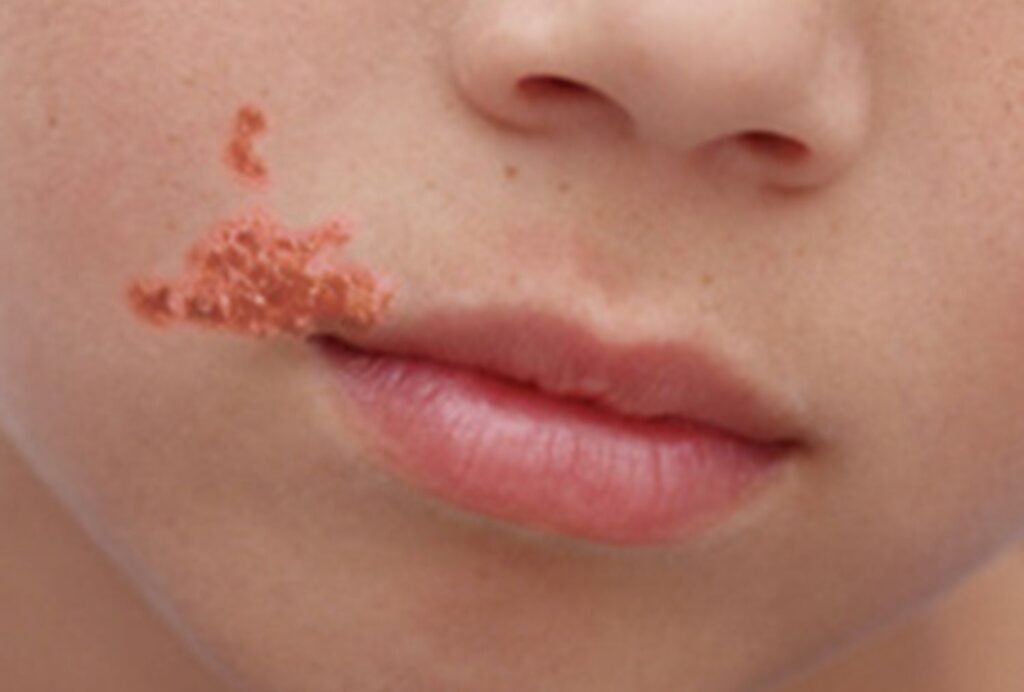
Common Types of Minor Bacterial Skin Infections
1. Impetigo
- Cause: Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes
- Symptoms: Red sores, honey-colored crusts, itching
- Treatment: Topical or oral antibiotics, hygiene maintenance
2. Folliculitis
- Cause: Infection of hair follicles by Staphylococcus aureus
- Symptoms: Small red bumps or pus-filled pustules around hair follicles
- Treatment: Antibacterial washes, warm compresses, topical antibiotics
3. Cellulitis
- Cause: Deep skin infection by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus
- Symptoms: Red, swollen, painful skin, fever, warmth at the affected site
- Treatment: Oral or intravenous antibiotics, rest, elevation of the affected area
4. Boils (Furuncles) and Carbuncles
- Cause: Staphylococcus aureus infection deep in hair follicles
- Symptoms: Painful, swollen lumps filled with pus, often clustered in carbuncles
- Treatment: Warm compresses, drainage, antibiotics if necessary
5. Erysipelas
- Cause: Streptococcus pyogenes
- Symptoms: Bright red, swollen, and sharply defined skin patches, fever, chills
- Treatment: Oral antibiotics, pain management, hydration
Causes and Risk Factors
- Poor hygiene
- Weakened immune system
- Skin injuries (cuts, insect bites, burns)
- Diabetes and chronic illnesses
- Close contact with infected individuals
- Excessive sweating and friction
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually based on clinical examination. In persistent or severe cases, a doctor may perform:
- Skin swabs or cultures to identify the bacteria
- Blood tests in cases of systemic infection
- Biopsy if deeper infection is suspected
Treatment Options
Home Remedies
- Cleaning the area with mild soap and water
- Applying warm compresses to reduce swelling
- Keeping the area dry and covered
- Over-the-counter antibiotic ointments
Medical Treatment
- Topical antibiotics for mild infections
- Oral antibiotics for moderate cases
- Intravenous antibiotics for severe infections
- Surgical drainage for large abscesses
Prevention Strategies
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Keep wounds clean and covered
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels and razors
- Wash hands frequently
- Boost immunity through a balanced diet and exercise
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- The infection spreads or worsens
- There is fever, severe pain, or swelling
- Red streaks appear around the infection site
- The wound does not heal within a few days
Minor bacterial skin infections are typically manageable with proper care. However, recognizing early signs and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent complications. Good hygiene and preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of bacterial infections and promote overall skin health.