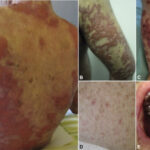
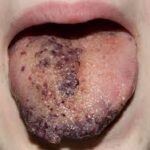
Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) is a rare inherited metabolic disorder that affects the body’s ability to break down certain proteins and fats. It results from a deficiency in the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase or defects in vitamin B12 metabolism. MMA leads to the accumulation of methylmalonic acid, causing severe metabolic acidosis and potential organ damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the condition.
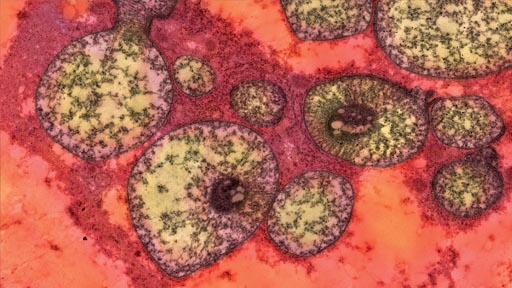
Causes and Genetic Basis of Methylmalonic Acidemia
MMA is primarily caused by mutations in the MUT, MMAA, MMAB, MMADHC, or MCEE genes. These genes are involved in the proper function of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase or its cofactor, adenosylcobalamin (a form of vitamin B12). The disorder follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, meaning both parents must carry a defective gene for the child to be affected.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
The severity of MMA symptoms varies depending on the type and genetic mutation involved. Common symptoms include:
- Failure to thrive – Poor growth and weight gain in infants
- Lethargy and developmental delay – Delayed milestones and reduced activity levels
- Vomiting and dehydration – Common due to metabolic crises
- Hypotonia (low muscle tone) – Leading to motor function impairment
- Neurological complications – Seizures, intellectual disabilities, and movement disorders
- Renal dysfunction – Kidney damage due to chronic acid buildup
Diagnosis and Newborn Screening
Early diagnosis through newborn screening programs is critical for preventing severe complications. Diagnostic tests include:
- Blood tests – Elevated methylmalonic acid levels in plasma
- Urine organic acid analysis – Detection of excess methylmalonic acid
- Genetic testing – Identifying mutations in MMA-related genes
- Enzyme activity assays – Assessing methylmalonyl-CoA mutase function
Treatment Options and Management
There is no definitive cure for MMA, but management strategies include:
1. Dietary Modifications
- Low-protein diet – Reducing intake of amino acids that contribute to MMA accumulation
- Medical formulas – Special metabolic formulas that provide essential nutrients while minimizing harmful substrates
2. Vitamin B12 Supplementation
Some MMA subtypes respond to hydroxycobalamin (B12 injections), particularly those caused by defects in vitamin B12 metabolism.
3. Pharmacological Interventions
- Carnitine supplementation – Helps eliminate toxic metabolites
- Metronidazole – Reduces the production of propionic acid by gut bacteria
4. Liver and Kidney Transplantation
In severe cases, liver or combined liver-kidney transplantation may be required to improve metabolic stability.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
With early intervention, individuals with MMA can lead relatively stable lives. However, complications such as chronic kidney disease and neurological impairments may persist. Regular monitoring and lifelong management are necessary to improve outcomes.
Methylmalonic acidemia is a complex metabolic disorder requiring early detection and continuous management. Advances in newborn screening, genetic research, and targeted therapies provide hope for improved patient outcomes. Continued research into gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapies may offer future curative options.