Methotrexate (MTX) is a widely used chemotherapeutic and immunosuppressive drug for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and various malignancies. However, methotrexate toxicity can occur due to overdose, impaired elimination, or drug interactions, leading to severe complications. Understanding its manifestations and treatment options is crucial for prevention and management.
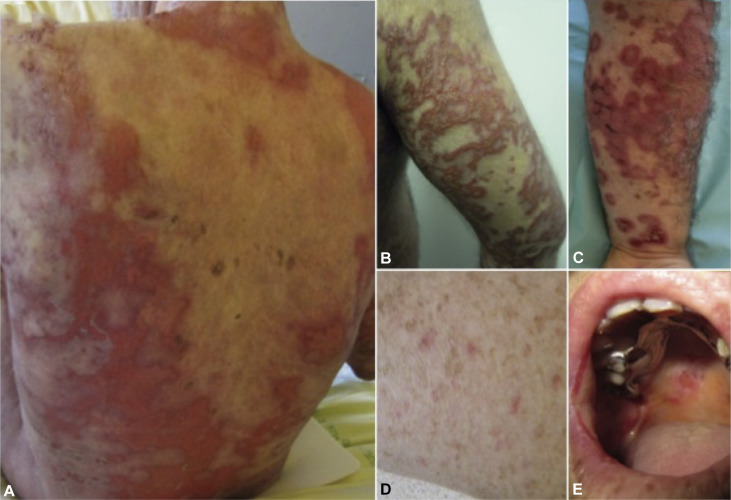
Causes and Risk Factors of Methotrexate Toxicity
Methotrexate toxicity arises from excessive drug accumulation in the body. Several factors contribute to toxicity, including:
- High-dose administration – Used in cancer therapy, increasing toxicity risk.
- Renal impairment – Reduced clearance leading to drug accumulation.
- Hepatic dysfunction – Compromised metabolism of methotrexate.
- Concomitant medications – Drugs such as NSAIDs, proton pump inhibitors, and sulfonamides interfere with methotrexate clearance.
- Dehydration and malnutrition – Increased susceptibility to toxicity.
- Age-related factors – Elderly patients have a higher risk due to physiological decline in drug metabolism.
Symptoms of Methotrexate Toxicity
Toxicity symptoms vary based on the affected organ system:
1. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Mucositis (oral ulcers)
2. Hematologic Toxicity
- Myelosuppression (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia)
- Increased risk of infections
3. Hepatic Toxicity
- Elevated liver enzymes (AST, ALT)
- Hepatitis
- Fibrosis with chronic exposure
4. Renal Toxicity
- Acute kidney injury
- Hematuria and proteinuria
5. Neurological Symptoms
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Seizures (in severe cases)
6. Pulmonary Toxicity
- Interstitial pneumonitis
- Dyspnea and cough
Diagnosis of Methotrexate Toxicity
1. Clinical Evaluation
A detailed history of methotrexate dosage, renal function, and concurrent medications is essential. Symptoms such as mucositis and hematologic abnormalities raise suspicion.
2. Laboratory Investigations
- Serum methotrexate levels – Helps assess drug accumulation.
- Complete blood count (CBC) – Identifies myelosuppression.
- Liver function tests (LFTs) – Evaluates hepatic injury.
- Renal function tests – Assesses nephrotoxicity.
3. Imaging Studies
- Chest X-ray and CT scans may be required in suspected pulmonary toxicity.
Treatment of Methotrexate Toxicity
1. Drug Discontinuation
Immediate cessation of methotrexate is crucial upon suspicion of toxicity.
2. Leucovorin (Folinic Acid) Rescue
Leucovorin counteracts methotrexate’s toxic effects by replenishing folate stores. It is administered based on serum methotrexate levels.
3. Glucarpidase Therapy
Glucarpidase enzymatically degrades methotrexate, aiding in rapid drug clearance, particularly in cases of renal failure.
4. Hydration and Alkalinization
Intravenous fluids and sodium bicarbonate help enhance methotrexate elimination through urine alkalinization.
5. Supportive Care
- Blood transfusions for anemia
- Antibiotics for infections due to immunosuppression
- Gastrointestinal protection with proton pump inhibitors
Prevention of Methotrexate Toxicity
- Routine Monitoring: Regular blood tests to assess renal function, liver enzymes, and CBC.
- Dose Adjustment: Individualized dosing based on renal function and drug interactions.
- Patient Education: Awareness of potential side effects and adherence to prescribed doses.
- Adequate Hydration: Prevents renal toxicity by enhancing drug elimination.
Methotrexate toxicity is a potentially life-threatening condition requiring early recognition and prompt intervention. Regular monitoring, patient education, and appropriate supportive therapy significantly reduce adverse outcomes. By understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive strategies, healthcare providers can enhance patient safety and treatment efficacy.