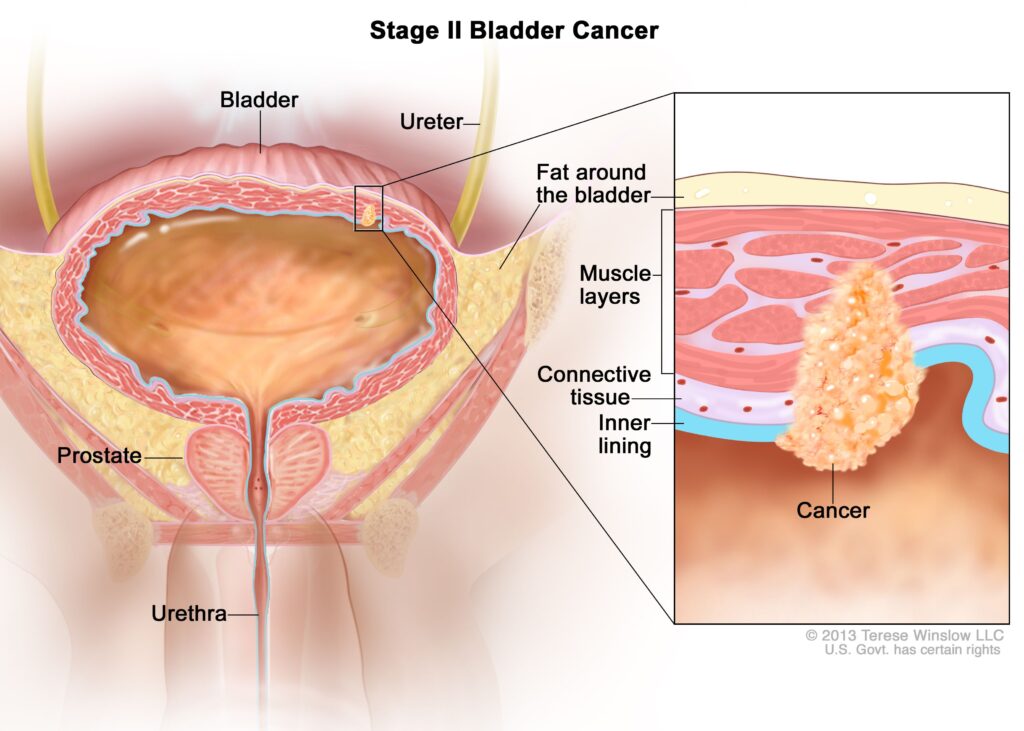
Metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC) is an advanced stage of urothelial cancer, primarily affecting the bladder but capable of spreading to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, and bones. This aggressive malignancy requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to improve patient outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Smoking: The leading risk factor, significantly increasing the chances of bladder cancer.
- Chemical Exposure: Prolonged exposure to industrial chemicals, such as aromatic amines found in dyes and paints, elevates risk.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions like chronic bladder infections or long-term catheter use contribute to the disease.
- Genetic Factors: Family history and genetic predispositions play a role.
Symptoms of Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination or urgency
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bone pain (if cancer has spread to bones)
Diagnosis and Staging
- Urinalysis & Cytology: Detects abnormal cells in urine.
- Cystoscopy: Direct visualization of the bladder using a camera.
- Biopsy: Confirms malignancy through tissue sampling.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans identify metastatic spread.
- Molecular Testing: Evaluates PD-L1 expression and FGFR mutations to guide targeted therapies.
Treatment Options
1. Chemotherapy
- Platinum-Based Regimens: Combination therapies using cisplatin or carboplatin remain the first-line treatment.
- Gemcitabine & Taxanes: Alternative options for patients ineligible for platinum therapy.
2. Immunotherapy
- PD-L1 Inhibitors: Atezolizumab and pembrolizumab have shown efficacy in patients resistant to chemotherapy.
- CTLA-4 Inhibitors: Being studied in clinical trials to enhance immune response.
3. Targeted Therapy
- FGFR Inhibitors: Erdafitinib is approved for patients with FGFR mutations.
- Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs): Enfortumab vedotin targets specific cancer cells, delivering cytotoxic agents.
4. Radiation Therapy
Used for symptom management in cases where surgery is not viable.
5. Surgery
In select cases, radical cystectomy (bladder removal) may be performed.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Survival rates depend on response to treatment, cancer stage, and overall health. Recent advancements in immunotherapy and targeted treatments have improved outcomes.
Emerging Research and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research focuses on novel combinations of immunotherapy and targeted drugs to enhance survival rates and reduce side effects. Patients may benefit from participation in clinical trials testing new therapeutic approaches.
Metastatic urothelial carcinoma is a challenging but increasingly treatable disease. Advances in personalized medicine, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies offer hope for improved patient outcomes. Early detection and a multidisciplinary approach are crucial in managing this aggressive cancer.