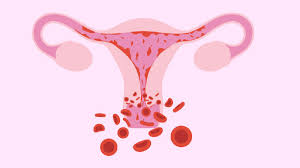
Menorrhagia is a common gynecological condition characterized by excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding. It affects many women and can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia can be caused by various medical conditions, including:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
- Estrogen and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle. Any imbalance can lead to excessive bleeding.
- Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders can contribute to hormonal fluctuations.
2. Uterine Fibroids and Polyps
- Noncancerous growths in the uterus can lead to heavy and prolonged bleeding.
- Endometrial polyps also contribute to abnormal menstrual flow.
3. Adenomyosis
- This condition occurs when endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, causing heavy and painful periods.
4. Bleeding Disorders
- Conditions like von Willebrand disease or platelet function disorders can lead to prolonged bleeding.
5. Medications and Medical Conditions
- Blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs may exacerbate bleeding.
- Liver and kidney diseases can interfere with blood clotting.
Symptoms of Menorrhagia
Women experiencing menorrhagia may notice:
- Menstrual bleeding lasting more than seven days.
- Passing large blood clots (larger than a quarter).
- Soaking through one or more sanitary pads or tampons every hour.
- Fatigue and shortness of breath due to anemia.
Diagnosis of Menorrhagia
To diagnose menorrhagia, a doctor may recommend:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
- Detailed questions about menstrual cycles, symptoms, and overall health.
- A pelvic exam to check for abnormalities.
2. Blood Tests
- Evaluates hemoglobin levels to check for anemia.
- Tests for blood clotting disorders.
3. Ultrasound and Imaging Tests
- Transvaginal ultrasound to assess the uterus, ovaries, and pelvic region.
- Sonohysterography to detect fibroids or polyps.
4. Endometrial Biopsy and Hysteroscopy
- A small tissue sample is taken to rule out endometrial hyperplasia or cancer.
- Hysteroscopy involves inserting a thin camera into the uterus for better visualization.
Treatment for Menorrhagia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms.
1. Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Reduce pain and blood loss.
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and hormonal patches regulate menstrual cycles.
- Tranexamic Acid: Helps reduce menstrual bleeding.
- Iron Supplements: Address anemia due to blood loss.
2. Surgical Options
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Removes excess tissue from the uterus.
- Endometrial Ablation: Destroys the uterine lining to reduce bleeding.
- Myomectomy: Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus in severe cases.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in iron to prevent anemia.
- Regular exercise to improve circulation and hormonal balance.
- Manage stress through meditation and relaxation techniques.
- Track menstrual cycles using a menstrual diary or app.
Menorrhagia is a treatable condition that requires timely medical intervention. Women experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding should consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and management can significantly improve quality of life.