Meibomianitis, also known as Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), is a common inflammatory condition affecting the Meibomian glands located along the eyelid margins. These glands are responsible for producing the oily component of tears, which prevents evaporation and maintains eye moisture. When these glands become inflamed or clogged, it leads to symptoms like dry eyes, irritation, and redness.
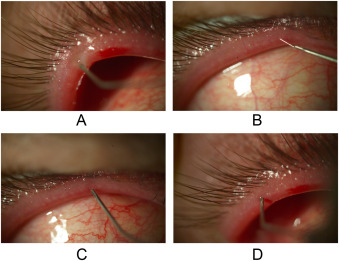
Causes of Meibomianitis
The primary cause of Meibomianitis is the dysfunction of the Meibomian glands, which can result from:
- Bacterial Infections: Overgrowth of bacteria on the eyelids can contribute to gland dysfunction.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions like rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis can exacerbate gland blockage.
- Aging: Gland function naturally declines with age.
- Hormonal Changes: Imbalances, especially during menopause, can lead to reduced oil production.
- Poor Eyelid Hygiene: Accumulation of debris and makeup can block the glands.
- Contact Lens Use: Prolonged use of contact lenses may impact Meibomian gland function.
Symptoms of Meibomianitis
Symptoms of Meibomianitis vary in severity but commonly include:
- Eye Redness and Irritation: Persistent discomfort and inflammation.
- Dry Eye Sensation: A gritty or burning feeling in the eyes.
- Blurry Vision: Due to unstable tear film.
- Eyelid Swelling: Puffiness around the eyelids.
- Increased Tear Production: The eyes may compensate for dryness by overproducing tears.
- Crusting on Eyelids: Especially noticeable upon waking.
Diagnosis of Meibomianitis
Diagnosis of Meibomianitis involves a comprehensive eye examination, which may include:
- Slit Lamp Examination: To assess the health of the Meibomian glands.
- Meibography: Imaging technique to visualize gland structure.
- Tear Film Analysis: To evaluate tear stability and composition.
- Expression Test: To check for gland blockages.
Treatment Options for Meibomianitis
Effective management of Meibomianitis involves a combination of home care and medical interventions:
Home Remedies and Self-Care
- Warm Compresses: Helps liquefy and unclog gland secretions.
- Eyelid Hygiene: Regular cleaning with baby shampoo or specialized eyelid cleansers.
- Omega-3 Supplements: Helps improve gland function and tear quality.
- Blinking Exercises: Encourages natural gland expression and secretion.
Medical Treatments
- Prescription Eye Drops: Lubricating drops or antibiotics for severe cases.
- Meibomian Gland Expression: Performed by an eye specialist to clear blockages.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: Reduces inflammation and improves gland function.
- LipiFlow Thermal Pulsation: Uses heat and massage to restore gland function.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures help reduce the risk of Meibomianitis recurrence:
- Maintain good eyelid hygiene.
- Avoid excessive screen time to reduce eye strain.
- Remove makeup thoroughly before sleeping.
- Stay hydrated and follow a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Possible Complications
If left untreated, Meibomianitis can lead to complications such as:
- Chronic Dry Eye Syndrome
- Recurrent Eye Infections
- Corneal Damage
- Blepharitis (Inflammation of the Eyelids)
Meibomianitis is a prevalent yet manageable condition that requires proactive care. By maintaining proper eyelid hygiene and seeking timely treatment, individuals can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Consulting an ophthalmologist for persistent symptoms is essential to ensure optimal eye health.