Measles and rubella are highly contagious viral infections that can cause severe complications, including pneumonia, encephalitis, congenital disabilities, and even death. The Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccine is a crucial public health intervention aimed at eradicating these diseases globally.
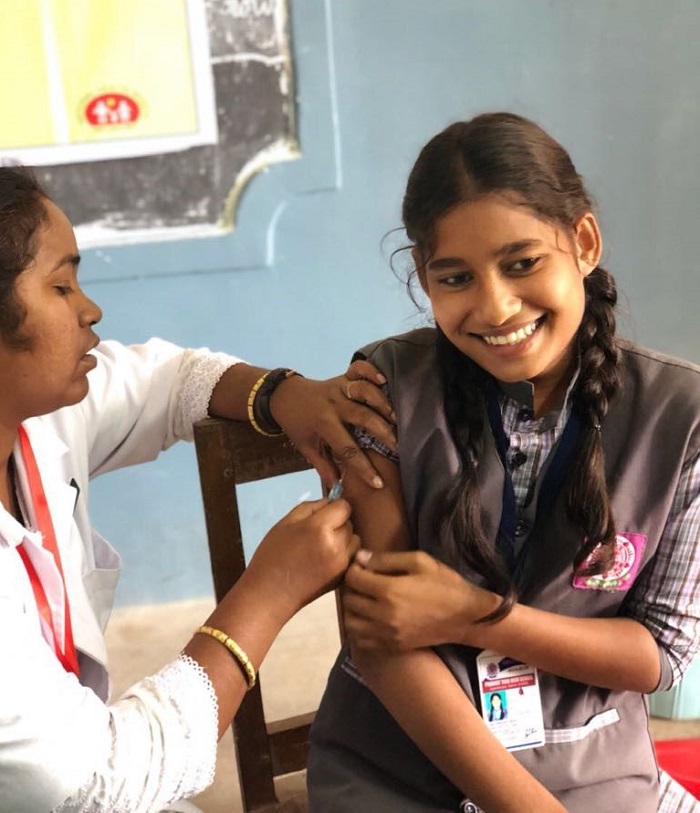

Why Measles-Rubella Vaccination is Essential
- Prevents Outbreaks: Large-scale vaccination programs have significantly reduced measles and rubella cases worldwide.
- Protects Pregnant Women and Infants: Rubella infection during pregnancy can cause congenital rubella syndrome (CRS), leading to severe birth defects.
- Reduces Mortality Rates: Measles-related deaths have declined by over 70% due to widespread vaccination.
- Promotes Herd Immunity: A high vaccination rate ensures that even unvaccinated individuals are protected.
Measles-Rubella Vaccine Schedule
The MR vaccine is typically administered in two doses:
- First Dose: At 9-12 months of age
- Second Dose: At 15-18 months or before school entry (4-6 years)
- Booster Doses: In some regions, an additional dose is given in adolescence to ensure long-term immunity.
MR Vaccine in Combination with Other Vaccines
The MR vaccine is often given as part of the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine, which provides protection against three viral infections in a single shot.
Effectiveness and Safety of the MR Vaccine
- High Efficacy: The MR vaccine is 97% effective in preventing measles and 95% effective against rubella.
- Minimal Side Effects: Mild fever, rash, or swelling at the injection site may occur but are temporary.
- Long-Term Protection: Immunity from MR vaccination generally lasts for decades, reducing the need for frequent booster doses.
Global Vaccination Efforts and Impact
WHO’s MR Elimination Strategy
The World Health Organization (WHO) has set ambitious goals to eliminate measles and rubella through mass immunization campaigns.
Key Strategies:
- Routine childhood immunization programs
- National and regional MR vaccination drives
- Surveillance and outbreak response strategies
- Public awareness campaigns to combat vaccine hesitancy
Impact of MR Vaccination Worldwide
- Over 23 million deaths have been prevented since 2000 through MR vaccination efforts.
- Several countries have achieved measles elimination status, with ongoing efforts to eradicate rubella globally.
- The Gavi Alliance and WHO have contributed to making MR vaccines more accessible in low-income countries.
Challenges in Achieving Full Immunization Coverage
Despite the benefits, challenges remain:
- Vaccine Hesitancy: Misinformation and fear surrounding vaccines hinder immunization rates.
- Access in Remote Areas: Limited healthcare infrastructure affects vaccine distribution.
- Conflict Zones and Humanitarian Crises: Displacement of populations disrupts vaccination programs.
The Need for Continued Vigilance
Measles-Rubella vaccination is a critical tool in global health efforts to eradicate preventable diseases. Governments, healthcare organizations, and communities must work together to ensure high immunization coverage and protect future generations.