Bilateral orchiectomy, often referred to as the removal of both testes, is a significant surgical procedure primarily used in the treatment of various conditions, such as testicular cancer, prostate cancer, and other medical scenarios involving hormone regulation. In this article, we will explore the procedure, its indications, benefits, potential risks, and recovery process, providing a thorough understanding of bilateral orchiectomy.
What is Bilateral Orchiectomy?
Bilateral orchiectomy is a surgical operation in which both testicles are removed. This procedure may be performed for various medical reasons, including the management of testicular cancer, hormone therapy for prostate cancer, or in some cases, gender-affirming surgery. By removing the testicles, the body’s production of testosterone is significantly reduced, which can help manage specific medical conditions.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves making an incision in the scrotum or abdomen to access the testes. Once the testes are removed, the surgeon will close the incision, and the patient will begin the recovery process.
Indications for Bilateral Orchiectomy
Bilateral orchiectomy is indicated in several conditions, including:
1. Testicular Cancer
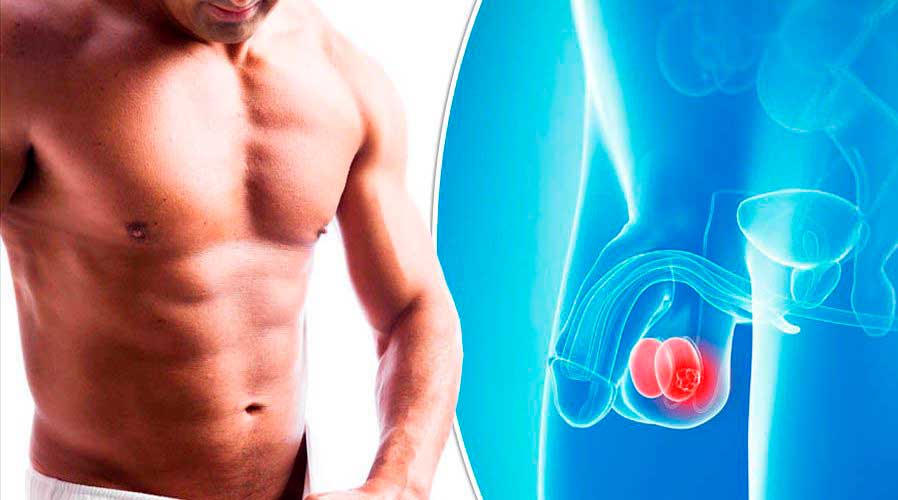
One of the most common reasons for performing a bilateral orchiectomy is the treatment of testicular cancer. If cancer is present in both testicles, or if the condition cannot be managed through other means, removal of both testicles may be necessary to prevent the spread of cancer.
2. Prostate Cancer Treatment
In advanced prostate cancer, bilateral orchiectomy is sometimes performed as a form of hormone therapy. The removal of the testicles reduces the body’s production of testosterone, which is known to fuel the growth of prostate cancer cells.
3. Gender-Affirming Surgery
For individuals transitioning from male to female, bilateral orchiectomy is often a step in the process of gender-affirming surgery. This procedure helps align an individual’s physical characteristics with their gender identity by removing the testes, thereby ceasing the production of male hormones.
4. Other Medical Conditions
In rare cases, bilateral orchiectomy may be recommended for other medical conditions that cause hormone imbalances or other reproductive health issues that cannot be addressed through less invasive treatments.
The Procedure: What to Expect
Bilateral orchiectomy is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is unconscious and pain-free during the procedure. The surgeon may make an incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen, depending on the patient’s specific circumstances and medical history.
Once the incision is made, the surgeon carefully removes both testicles. After removal, the surgical site is closed with sutures, and the patient is moved to a recovery room for monitoring as they wake from anesthesia.
The entire procedure typically lasts between one to two hours, although the exact duration can vary depending on individual factors.
Potential Risks and Complications
While bilateral orchiectomy is generally considered safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks. These can include:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding may occur, requiring medical intervention.
- Hormonal Imbalance: The removal of the testes causes a dramatic reduction in testosterone levels, which can lead to various symptoms, such as hot flashes, decreased libido, and mood swings.
- Emotional and Psychological Effects: The removal of both testicles can have significant emotional and psychological effects, particularly in cases where the procedure is related to cancer or gender-affirming surgery. Counseling and support are often recommended to help individuals cope with these changes.
- Changes in Sexual Function: In some cases, the removal of the testicles may impact sexual function and fertility. However, many patients find ways to manage these changes through hormone replacement therapy or other methods.
Hormone Therapy and Post-Operative Care
Following a bilateral orchiectomy, patients will often require hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to compensate for the loss of testosterone production. This can help alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and reduced libido.
In cases where the surgery is performed as a treatment for prostate cancer, hormone therapy may be an essential component of the overall treatment plan. For individuals undergoing gender-affirming surgery, hormone therapy may also be a vital aspect of their transition process.
The recovery period after a bilateral orchiectomy generally involves rest and limited physical activity for several weeks. Pain management, wound care, and monitoring for signs of infection are essential during this phase.
Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline after bilateral orchiectomy can vary from person to person, but here is a general overview:
1. Immediate Post-Operative Care
Patients will typically remain in the hospital for a few hours after the procedure for monitoring. Pain medications will be prescribed to manage any discomfort, and patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities during this time.
2. First Week
During the first week of recovery, swelling and bruising around the incision site are common. Patients should follow their surgeon’s advice on wound care, avoid lifting heavy objects, and rest as much as possible.
3. One to Two Months
Most patients can return to work and normal activities within 4-6 weeks, but it may take up to two months for full recovery. Testosterone levels may start to stabilize with hormone therapy, and patients may begin to adjust to any physical and emotional changes.
4. Long-Term Recovery
Long-term recovery from a bilateral orchiectomy may involve ongoing medical management, including hormone therapy and emotional support. For cancer patients, regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor for recurrence.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The emotional and psychological impact of a bilateral orchiectomy can be profound, especially in cases related to cancer or gender-affirming surgery. For cancer patients, the procedure may symbolize a significant loss and the end of fertility, while transgender individuals may experience a sense of alignment with their gender identity.
Counseling, therapy, and support groups can be beneficial for individuals adjusting to the emotional and psychological changes that accompany this procedure. Support from loved ones and healthcare professionals is crucial during this time.
Bilateral orchiectomy is a critical surgical procedure for many individuals facing testicular cancer, prostate cancer, or undergoing gender-affirming surgery. Understanding the procedure, its indications, potential risks, and recovery process is essential for anyone considering or preparing for this surgery. With the right medical care, support, and post-operative management, patients can navigate the physical, emotional, and psychological challenges associated with this procedure and continue their path toward healing and well-being.