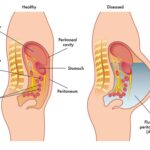
Malignancy refers to cancerous growths that have the potential to invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to distant body parts. Unlike benign tumors, malignant cells exhibit uncontrolled division and spread, making them a critical concern in oncology. Understanding malignancy helps in early detection and effective treatment.
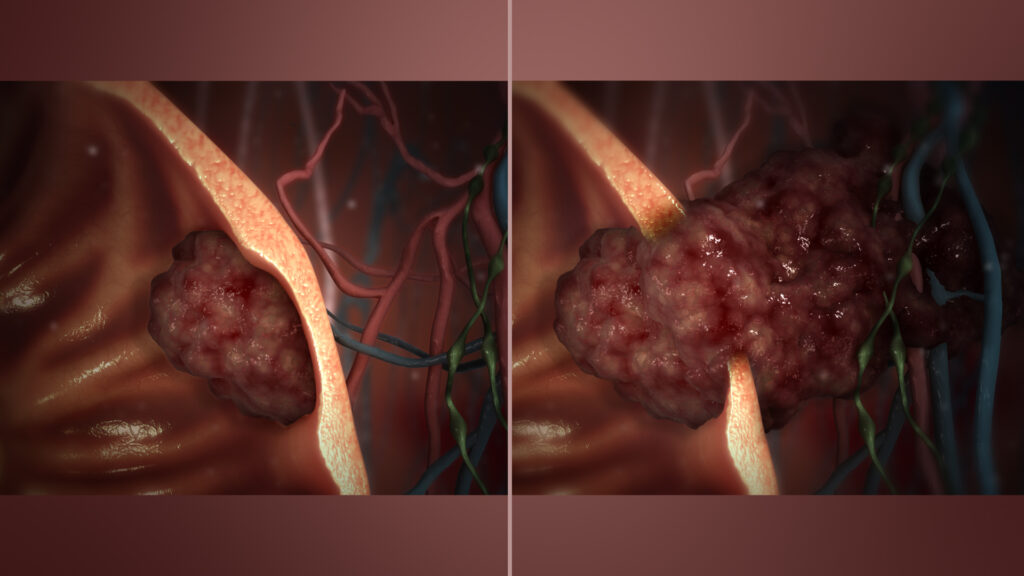
Causes and Risk Factors of Malignancy
Malignancies arise due to genetic mutations and environmental factors. Common risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of cancer increases risk.
- Carcinogens: Exposure to tobacco, radiation, and chemicals.
- Infections: HPV, Hepatitis B and C, and Helicobacter pylori.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor diet, obesity, and lack of exercise.
- Chronic inflammation: Conditions like ulcerative colitis increase malignancy risk.
Symptoms of Malignancy
Symptoms vary based on cancer type and location. General signs include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Pain and swelling
- Unusual lumps
- Changes in skin appearance
- Prolonged cough or voice changes
Diagnosis of Malignancy
Doctors use multiple diagnostic tools to detect malignancies:
- Imaging tests: MRI, CT scans, X-rays
- Biopsy: Tissue sample examination
- Blood tests: Tumor markers like PSA, CEA
- Endoscopy: Internal imaging of affected areas
Types of Malignant Tumors
1. Carcinomas
- Originating in epithelial cells, affecting organs like the lungs, breasts, and colon.
2. Sarcomas
- Developing in connective tissues like bones, muscles, and cartilage.
3. Leukemias
- Blood cancer affecting bone marrow and circulating blood cells.
4. Lymphomas
- Cancer originating in the lymphatic system, including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Treatment Options for Malignancy
1. Surgery
- Effective for localized tumors, removing malignant tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy
- Involves drugs that kill or slow cancer cell growth.
4. Immunotherapy
- Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells.
5. Targeted Therapy
- Uses drugs designed to attack specific genetic markers in cancer cells.
Prevention Strategies for Malignancy
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
2. Early Detection and Screening
- Routine screenings such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap smears.
- Genetic testing for individuals with a family history.
3. Vaccination
- HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines reduce cancer risk.
Malignancy remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, but advancements in medical science continue to improve diagnosis and treatment outcomes. Awareness, early detection, and proactive healthcare can significantly reduce risks and enhance survival rates.