Listeriosis is a serious foodborne illness caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. While relatively rare, it poses significant health risks, particularly to vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, newborns, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Understanding the intricacies of listeriosis is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Etiology and Transmission
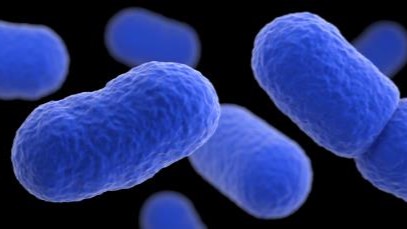
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive bacterium found ubiquitously in environments like soil, water, and decaying vegetation. Humans typically contract listeriosis through the consumption of contaminated food products. Common sources include:
- Unpasteurized Dairy Products: Milk and cheeses made from raw milk.
- Ready-to-Eat Meats: Deli meats and hot dogs that are not adequately heated.
- Seafood: Smoked or raw seafood products.
- Produce: Contaminated fruits and vegetables.
The bacterium’s resilience allows it to survive and even grow under refrigeration temperatures, making it a formidable pathogen in food safety.
Clinical Manifestations
The symptoms of listeriosis can vary based on the affected individual and the severity of the infection.
- Invasive Listeriosis: This severe form occurs when the infection spreads beyond the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms include:
- Fever and Muscle Aches: Often accompanied by fatigue.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headache, stiff neck, confusion, loss of balance, and convulsions, indicative of meningitis or encephalitis.
- Pregnancy-Related Complications: In pregnant women, listeriosis may lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, premature delivery, or life-threatening infection of the newborn.
- Non-Invasive Listeriosis: A milder form presenting as gastroenteritis with symptoms such as:
- Diarrhea: Often self-limiting.
- Fever: Mild and transient.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of listeriosis involves:
- Microbiological Cultures: Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or amniotic fluid confirms the diagnosis.
- Imaging Studies: In cases of neurological involvement, imaging may be utilized to assess the extent of infection.
Treatment
Prompt initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy is vital. The standard treatment regimen includes:
- Ampicillin: Often administered intravenously.
- Gentamicin: Frequently added for its synergistic effects.
The duration of therapy varies based on the severity and site of infection but typically ranges from 2 to 6 weeks.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing listeriosis centers on minimizing exposure to Listeria monocytogenes through:
- Food Handling and Preparation:
- Thorough Cooking: Ensure all meats and seafood are cooked to safe temperatures.
- Proper Storage: Refrigerate perishable items promptly and maintain refrigerator temperatures at or below 40°F (4°C).
- Avoid Cross-Contamination: Use separate cutting boards for raw and cooked foods.
- Dietary Precautions for High-Risk Groups:
- Avoid Unpasteurized Products: Refrain from consuming raw milk and cheeses made from it.
- Limit Certain Ready-to-Eat Foods: Avoid deli meats, unless heated until steaming hot, and refrigerated smoked seafood.
Recent Outbreaks and Public Health Response
Listeriosis outbreaks, though infrequent, have significant public health implications. For instance, a recent outbreak linked to contaminated desserts in NHS hospitals resulted in multiple fatalities and hospitalizations. Such incidents underscore the importance of stringent food safety protocols and prompt public health interventions.
Listeriosis remains a formidable foodborne illness with the potential for severe outcomes, especially among vulnerable populations. Awareness of its sources, clinical manifestations, and preventive measures is essential for reducing its incidence and safeguarding public health.