Leukopenia, characterized by a diminished white blood cell (WBC) count, compromises the body’s immune defense, increasing susceptibility to infections. This article provides an in-depth exploration of leukopenia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding Leukopenia: A Comprehensive Overview
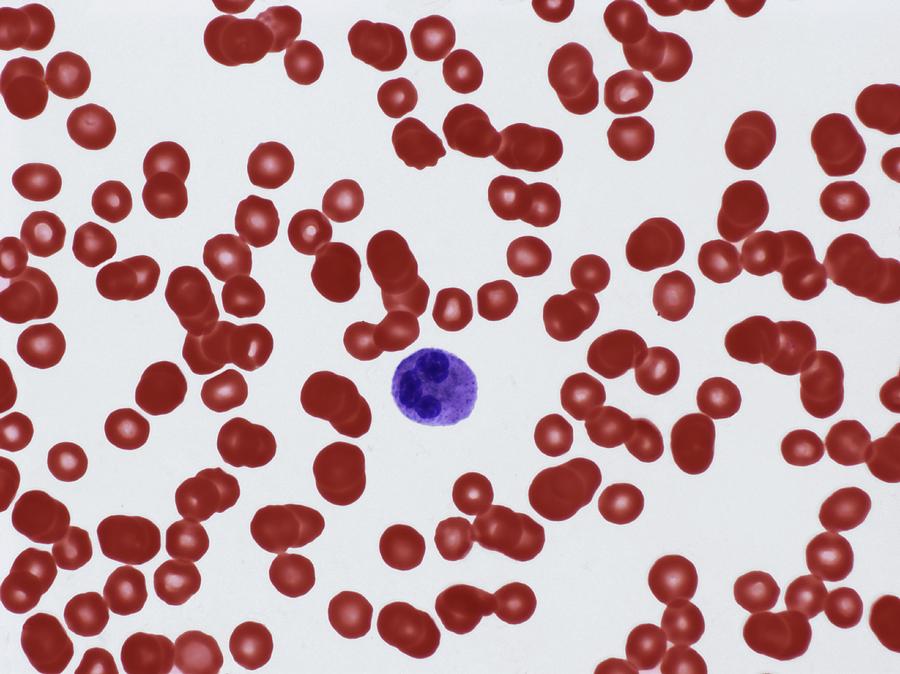
Leukopenia refers to a condition where the WBC count falls below the normal range, typically defined as fewer than 4,000 cells per microliter of blood. White blood cells are pivotal in combating infections; thus, a reduced count can significantly impair the immune response.
Etiology: Identifying the Causes of Leukopenia
Various factors can lead to leukopenia, including:
- Bone Marrow Disorders: Conditions such as aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes hinder the production of WBCs.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Disorders like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis may cause the immune system to attack WBCs.
- Infections: Viral infections, including HIV, can result in decreased WBC counts.
- Medications and Treatments: Chemotherapy and certain drugs can suppress bone marrow activity, leading to leukopenia.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals can impair WBC production.
Clinical Manifestations: Recognizing Symptoms of Leukopenia
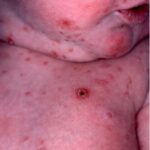
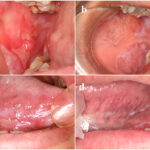
While leukopenia itself may not present noticeable symptoms, it predisposes individuals to infections. Common signs of infection associated with low WBC counts include:
- Fever and chills
- Sore throat
- Mouth ulcers
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Skin infections
Prompt medical attention is crucial upon experiencing these symptoms.
Diagnostic Approaches: Evaluating Leukopenia
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures WBC levels and identifies specific deficiencies.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Assesses bone marrow function and identifies underlying disorders.
- Additional Tests: Depending on suspected causes, tests for infections, autoimmune conditions, or nutritional deficiencies may be conducted.
Therapeutic Strategies: Managing and Treating Leukopenia
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause:
- Infection Management: Administration of antibiotics or antiviral medications as needed.
- Growth Factors: Medications like granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSFs) stimulate WBC production.
- Adjusting Medications: Modifying or discontinuing drugs that contribute to leukopenia.
- Nutritional Support: Supplementing deficiencies to promote bone marrow health.
Preventive Measures: Reducing the Risk of Leukopenia
To minimize infection risk:
- Practice diligent hand hygiene.
- Stay current with vaccinations.
- Avoid contact with individuals who are ill.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Implement safety measures to prevent injuries and infections.
Leukopenia signifies a critical reduction in white blood cells, undermining the immune system’s ability to combat infections. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and pursuing appropriate diagnostic and treatment strategies are essential for effective management. Adopting preventive practices further supports overall health and reduces infection risks associated with leukopenia.