Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome (LGS) is a rare and severe form of epilepsy that typically begins in early childhood. It is characterized by multiple seizure types, cognitive impairment, and resistance to standard anti-seizure medications. Managing LGS requires a multifaceted treatment approach, often including adjunct therapies to improve seizure control and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
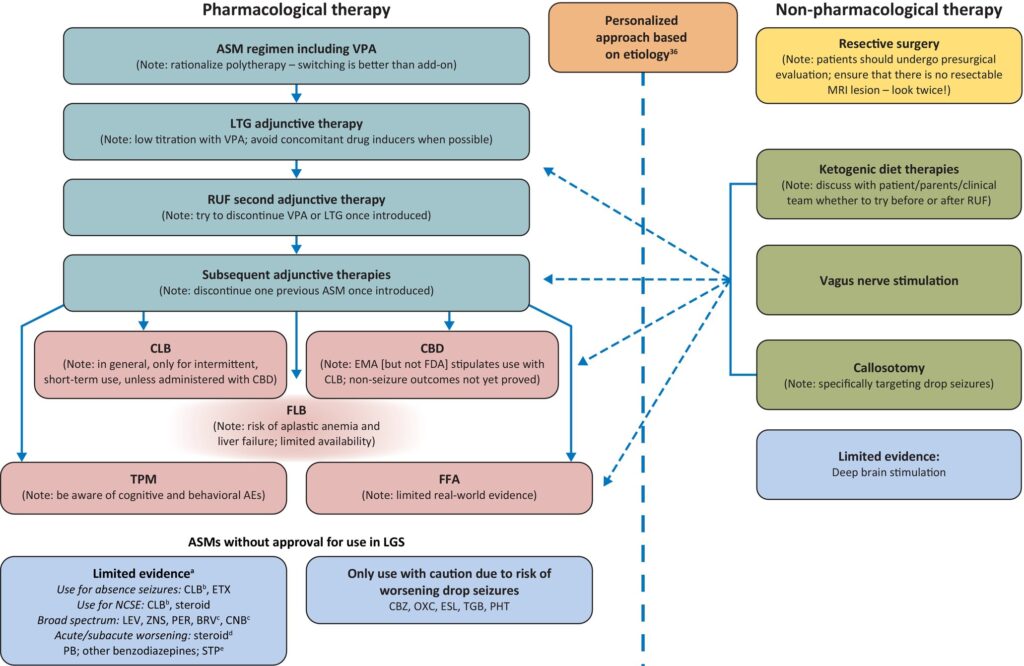
Primary Treatment Approaches for LGS
1. First-Line Anti-Seizure Medications
The initial management of LGS involves anti-seizure medications (ASMs), though many cases exhibit resistance to monotherapy. Commonly prescribed ASMs include:
- Valproate (Valproic Acid) – Often the first-line treatment for its broad-spectrum efficacy.
- Clobazam (Onfi) – A benzodiazepine used in combination with other ASMs.
- Lamotrigine (Lamictal) – Effective in reducing seizure frequency, especially tonic seizures.
- Rufinamide (Banzel) – Approved specifically for LGS, particularly beneficial for drop seizures.
- Topiramate (Topamax) – Used in polytherapy for seizure reduction.
Despite these treatments, many LGS patients experience persistent seizures, necessitating adjunct therapies.
Adjunctive Therapies for Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
2. Cannabidiol (CBD) for LGS
Epidiolex, a purified cannabidiol (CBD) formulation, has been FDA-approved for LGS treatment. It has shown significant efficacy in reducing seizure frequency, particularly drop seizures, without causing severe sedation.
3. Ketogenic Diet
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet is an effective adjunct therapy for LGS, particularly in drug-resistant cases. The diet promotes ketosis, which can reduce seizure frequency in some patients.
4. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Therapy
VNS therapy involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, helping to control seizures. It is recommended for patients with drug-resistant epilepsy and can be used alongside ASMs.
5. Corpus Callosotomy Surgery
For severe cases, a corpus callosotomy may be performed. This surgical procedure involves severing the corpus callosum to prevent seizure spread, particularly effective in controlling atonic seizures.
6. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS is an emerging treatment where electrodes are implanted in specific brain regions to regulate abnormal electrical activity, offering potential benefits for refractory LGS cases.
Future Developments in LGS Treatment
Advancements in gene therapy, precision medicine, and targeted neuromodulation are being explored for more effective LGS treatments. Clinical trials continue to investigate novel therapies aimed at improving seizure control and cognitive function.
Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome is a challenging condition requiring a combination of medical, dietary, and surgical interventions. While no cure exists, adjunct therapies significantly enhance seizure management and patient quality of life. Families and caregivers should work closely with neurologists to customize an optimal treatment plan for each individual case.