Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious complication following knee replacement surgery. It occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, typically in the legs, leading to potential complications such as pulmonary embolism (PE). Preventing DVT is crucial for ensuring a smooth and safe recovery.
Risk Factors for DVT After Knee Replacement
Several factors increase the risk of DVT post-surgery, including:
- Prolonged immobility – Reduced movement after surgery slows blood circulation.
- Surgical trauma – The procedure affects blood vessels and increases clotting risk.
- Obesity – Higher body weight contributes to poor circulation.
- Age – Older patients have a higher likelihood of developing blood clots.
- Previous history of DVT or clotting disorders – Personal or family history raises risk.
- Smoking – Nicotine constricts blood vessels, increasing clot risks.
- Dehydration – Thickened blood increases clot formation potential.
Effective Strategies for Preventing DVT Post-Knee Replacement
1. Early Mobilization and Physical Therapy
Encouraging movement as soon as possible post-surgery helps reduce DVT risk. Recommended activities include:
- Ankle pumps – Moving ankles up and down improves circulation.
- Quadriceps sets – Strengthens leg muscles and enhances blood flow.
- Walking with support – Gradually increasing movement speeds up recovery.
- Range-of-motion exercises – Prevents stiffness and promotes venous return.
2. Use of Blood Thinners (Anticoagulant Therapy)
Doctors often prescribe anticoagulants to reduce clot formation, including:
- Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH)
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like apixaban or rivaroxaban
- Aspirin therapy (in some cases for low-risk patients)
3. Compression Therapy: Stockings and Devices
Graduated compression stockings and pneumatic compression devices enhance circulation and reduce clotting risks by applying gentle pressure to the legs.
4. Adequate Hydration and Healthy Diet
Drinking sufficient fluids keeps blood viscosity low, while a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, leafy greens, and whole grains supports overall circulatory health.
5. Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking constricts blood vessels, and excessive alcohol can lead to dehydration, both increasing DVT risk. Eliminating these habits aids in a safer recovery.
6. Monitoring for Symptoms of DVT
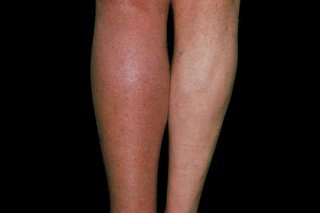
Early detection of DVT symptoms is crucial. Common warning signs include:
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Pain or tenderness, especially when standing or walking
- Red or discolored skin
- A feeling of warmth in the affected area
If any symptoms appear, immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent complications like pulmonary embolism.
7. Regular Follow-Ups with Your Doctor
Scheduled check-ups allow healthcare providers to assess recovery progress, adjust medications, and address potential concerns related to DVT risk.
Preventing deep vein thrombosis after knee replacement requires a combination of movement, medication, compression therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. By following these preventive strategies and staying vigilant for symptoms, patients can significantly lower their risk of DVT and ensure a smooth recovery. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized prevention plans.