Prostatitis, characterized by inflammation of the prostate gland, presents a significant urological concern among men. Among the bacterial pathogens implicated, Klebsiella pneumoniae has emerged as a notable causative agent, particularly in complicated cases. This article provides an in-depth exploration of Klebsiella prostatitis, focusing on its pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnostic methodologies, therapeutic interventions, and preventive strategies.
Pathogenesis of Klebsiella Prostatitis
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, encapsulated bacterium commonly residing in the human gastrointestinal tract. Its role in prostatitis involves several mechanisms:
- Ascending Infection: The bacterium can ascend from the urethra into the prostate, especially following urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Hematogenous Spread: In some instances, K. pneumoniae disseminates via the bloodstream, leading to prostatic infection. Notably, hypervirulent strains have been associated with metastatic infections, including prostate abscesses.
- Biofilm Formation: The ability to form biofilms enhances bacterial adherence and resistance to host defenses and antibiotics, complicating treatment.
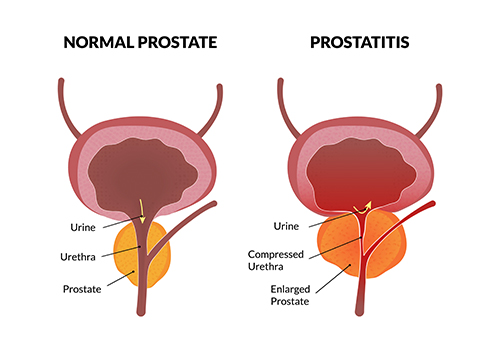
Clinical Manifestations
The presentation of Klebsiella prostatitis varies based on the infection’s acuity:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Systemic Symptoms: Fever, chills, malaise.
- Urinary Symptoms: Dysuria, frequency, urgency, and possible urinary retention.
- Pelvic Discomfort: Pain in the perineum, lower back, or genital area.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Recurrent UTIs: Persistent or recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic discomfort in the pelvic region.
- Voiding Dysfunction: Symptoms such as hesitancy or interrupted flow.
Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis is pivotal for effective management:
- Urine Cultures: Identification of K. pneumoniae in midstream urine samples aids in confirming the diagnosis.
- Prostatic Fluid Analysis: Examination of expressed prostatic secretions can reveal elevated white blood cell counts and the presence of the pathogen.
- Imaging Studies: In suspected prostate abscesses, imaging modalities like transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) or computed tomography (CT) scans are instrumental in detection.
Treatment Strategies
Management of Klebsiella prostatitis necessitates a tailored approach:
- Antibiotic Therapy:
- Acute Infections: Empirical broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone or ciprofloxacin, are initiated, followed by oral agents based on susceptibility profiles.
- Chronic Infections: Prolonged courses of oral antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are commonly employed.
- Addressing Antibiotic Resistance:
- ESBL-Producing Strains: Infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing K. pneumoniae may require alternative agents like carbapenems.
- Hypervirulent Strains: These may necessitate combination therapies and extended treatment durations due to increased virulence and resistance patterns.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of prostatic abscesses or when medical therapy fails, drainage procedures or surgical intervention may be warranted.
Preventive Measures
Preventing Klebsiella prostatitis involves several strategies:
- Prompt Treatment of UTIs: Early and appropriate management of urinary tract infections can reduce the risk of ascending prostatic infections.
- Aseptic Techniques: Ensuring sterile procedures during catheterization or urological interventions minimizes infection risks.
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Judicious use of antibiotics helps in curbing the development of resistant Klebsiella strains.
- Regular Monitoring: For individuals with recurrent prostatitis or underlying urological conditions, periodic evaluations can facilitate early detection and intervention.
Klebsiella pneumoniae prostatitis represents a complex clinical entity requiring a nuanced understanding of its pathogenesis, timely diagnosis, and tailored therapeutic strategies. Awareness of emerging resistant and hypervirulent strains is crucial for effective management and underscores the importance of preventive measures in mitigating this challenging infection.