Klebsiella pneumoniae osteomyelitis is a rare but severe bacterial infection affecting the bones. Klebsiella pneumoniae, a gram-negative pathogen known for its multidrug resistance, can cause significant complications if not promptly diagnosed and treated. It primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or recent surgical procedures. Understanding the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and appropriate treatment strategies is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What is Klebsiella pneumoniae Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis refers to a bacterial infection of the bone, leading to inflammation, bone destruction, and potential systemic complications. When caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae, the infection tends to be more aggressive due to the bacterium’s ability to resist multiple antibiotics. This condition can develop through direct contamination (trauma, surgery) or hematogenous spread from other infected sites.
Causes and Risk Factors
Primary Causes
- Hematogenous Spread: Bacteria enter the bloodstream from infections like pneumonia or urinary tract infections and reach the bones.
- Direct Inoculation: Trauma, fractures, or surgical procedures introduce bacteria into the bone.
- Contiguous Spread: Infections in adjacent soft tissues, such as diabetic foot ulcers, spread to bones.
Risk Factors
- Diabetes mellitus – Increased susceptibility due to poor circulation and immune dysfunction
- Immunosuppression – Patients undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplants, or with HIV/AIDS
- Recent orthopedic surgery – Surgical implants can act as a nidus for infection
- Peripheral vascular disease – Poor blood supply impairs infection clearance
- Chronic wounds or pressure ulcers – Serve as entry points for bacteria
Symptoms of Klebsiella pneumoniae Osteomyelitis
The clinical presentation varies depending on the infection site and duration. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent bone pain, localized swelling, and tenderness
- Fever, chills, and general malaise
- Redness and warmth over the affected bone
- Restricted range of motion if the infection involves joints
- Drainage of pus from an open wound in severe cases
Diagnosis and Laboratory Tests
Clinical Evaluation
- Detailed patient history, focusing on recent infections, trauma, or surgeries
- Physical examination to identify localized pain, swelling, and systemic symptoms
Laboratory and Imaging Tests
- Blood Tests: Elevated white blood cell count (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) indicate inflammation.
- Blood Cultures: Identify Klebsiella pneumoniae and its antibiotic susceptibility.
- Bone Biopsy and Culture: Confirms bacterial presence and guides targeted therapy.
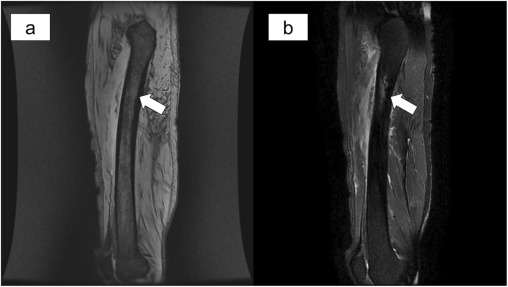
- MRI and CT Scan: Detects bone destruction, abscesses, and soft tissue involvement.
Treatment Strategies
Antibiotic Therapy
Treatment should be guided by bacterial culture results to ensure efficacy against drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Commonly used antibiotics include:
- Carbapenems (Imipenem, Meropenem): Effective against multidrug-resistant strains
- Fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin): Used in less severe infections
- Aminoglycosides (Amikacin): Often used in combination therapy
- Cephalosporins (Cefepime, Ceftazidime): Broad-spectrum coverage
Surgical Intervention
- Debridement: Removal of infected bone and necrotic tissue
- Bone Grafting: If extensive bone loss occurs, reconstructive procedures may be needed
- Amputation: In severe cases where infection is uncontrollable
Supportive Care
- Pain Management: NSAIDs or opioids for severe pain
- Wound Care: Proper dressing and infection control measures
- Nutritional Support: High-protein diet to promote bone healing
Complications of Untreated Osteomyelitis
Failure to treat Klebsiella pneumoniae osteomyelitis effectively can lead to:
- Chronic Osteomyelitis: Persistent infection causing bone destruction
- Septic Arthritis: Spread to nearby joints, leading to severe inflammation
- Bone Abscess Formation: Pockets of pus requiring surgical drainage
- Sepsis: Life-threatening systemic infection if bacteria enter the bloodstream
Prevention Strategies
Infection Control Measures
- Strict Aseptic Techniques: During surgeries and wound management
- Proper Wound Care: Cleaning and dressing open wounds to prevent bacterial entry
- Early Treatment of Infections: Prevents hematogenous spread to bones
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diabetes Management: Controlling blood sugar levels reduces the risk of infections
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Especially for patients with risk factors like vascular disease
- Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol: Promotes better immune function and circulation
Klebsiella pneumoniae osteomyelitis is a rare but serious bone infection requiring early diagnosis and aggressive treatment. Due to the bacterium’s resistance to multiple antibiotics, culture-guided therapy and, in some cases, surgical intervention are crucial for successful management. Preventive measures, including proper wound care and infection control, play a key role in reducing the risk of developing this condition.