Appendicitis is a common medical emergency, but complications arise when bacterial infections, such as those caused by Klebsiella species, lead to severe outcomes. Klebsiella complicated appendicitis involves infections that may result in perforation, abscess formation, or even sepsis. Understanding the role of Klebsiella in appendicitis is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
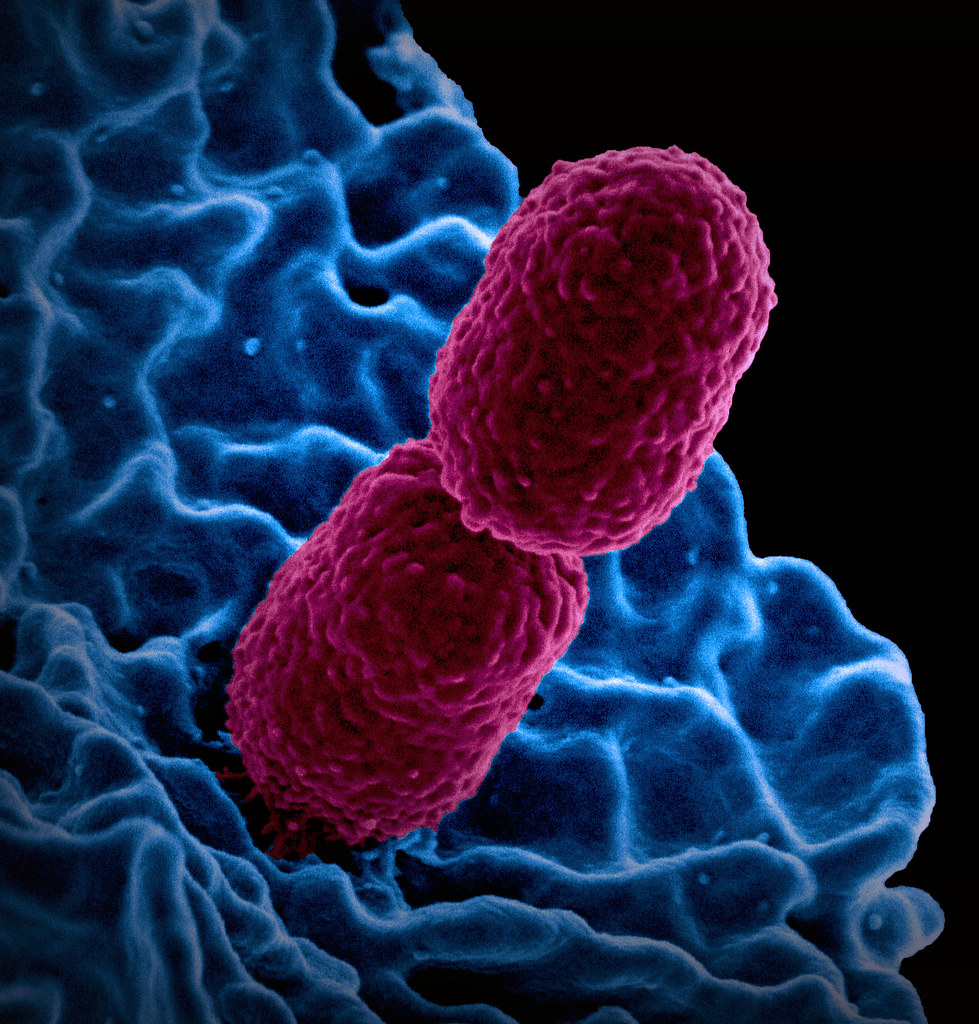
Understanding Klebsiella-Associated Appendicitis
Klebsiella species, particularly Klebsiella pneumoniae, are Gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. While generally harmless in healthy individuals, they can become opportunistic pathogens, leading to severe infections in immunocompromised patients.
When Klebsiella invades the appendix, it can accelerate tissue destruction, increase the risk of rupture, and contribute to post-surgical infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Bacterial Colonization and Overgrowth
- Klebsiella can overgrow in the gut due to antibiotic resistance or immune suppression.
- The bacteria thrive in anaerobic conditions, exacerbating appendiceal inflammation.
2. Perforation and Abscess Formation
- Infections with Klebsiella increase the likelihood of perforated appendicitis.
- Abscesses in the peritoneal cavity can develop, complicating surgical treatment.
3. Antibiotic Resistance
- Many Klebsiella strains produce extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), making them resistant to standard antibiotics.
- This resistance limits treatment options, requiring specialized antimicrobial therapy.
4. Immune System Deficiencies
- Diabetes, chronic diseases, and immunosuppressive therapies increase susceptibility to Klebsiella infections.
- Patients with hospital-acquired infections are at a higher risk.
Symptoms of Klebsiella Complicated Appendicitis
Symptoms of complicated appendicitis due to Klebsiella are often more severe than uncomplicated cases.
Primary Symptoms:
- Persistent, sharp abdominal pain, usually in the lower right quadrant
- High fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal bloating and tenderness
Signs of Severe Infection:
- Septic shock (low blood pressure, confusion, rapid heart rate)
- Peritonitis (rigid abdomen, extreme pain)
- Formation of intra-abdominal abscesses
Diagnosis of Klebsiella Complicated Appendicitis
1. Clinical Examination
- Physical assessment for tenderness and guarding in the lower right abdomen
- Positive McBurney’s point tenderness test
2. Laboratory Tests
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Elevated white blood cell count indicates infection
- Blood Cultures: Identifies Klebsiella species in bloodstream infections
- C-reactive Protein (CRP) and Procalcitonin: Markers of severe bacterial infection
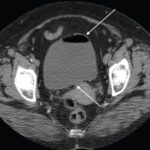
3. Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound: Detects inflamed or perforated appendix
- CT Scan: Confirms abscess formation and identifies complications
- MRI (for pregnant patients): Safe imaging alternative for detecting infection
Treatment Strategies
1. Emergency Appendectomy
Surgical removal of the appendix is the definitive treatment. Two primary approaches include:
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Preferred for lower complication rates and faster recovery
- Open Appendectomy: Used in cases of perforation or widespread infection
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Given the antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella, treatment must be tailored based on culture sensitivity.
- First-line options: Carbapenems (e.g., meropenem, imipenem)
- Alternative choices: Piperacillin-tazobactam or aminoglycosides for multidrug-resistant strains
- Combination Therapy: Often required in ESBL-producing Klebsiella infections
3. Management of Post-Surgical Infections
- Drainage of abscesses if present
- Prolonged IV antibiotic courses
- Supportive care for septic patients
4. Prevention of Recurrence
- Proper perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis
- Strict infection control in healthcare settings
- Monitoring for antibiotic resistance patterns
Klebsiella complicated appendicitis presents a significant challenge due to its potential for rapid progression, perforation, and antibiotic resistance. Early diagnosis, prompt surgical intervention, and tailored antibiotic therapy are crucial in managing this condition effectively. By understanding the risks associated with Klebsiella infections, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes and reduce post-surgical complications.