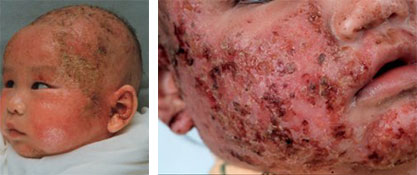
Eczema, clinically known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by redness, itching, and dryness. While many individuals experience manageable symptoms, a subset of patients endures intractable eczema, where conventional treatments fail to provide relief. This article delves into the complexities of intractable eczema, exploring its causes, challenges, and advanced therapeutic approaches.
Defining Intractable Eczema
Intractable eczema refers to cases unresponsive to standard treatments, leading to persistent discomfort and a diminished quality of life. This refractory nature necessitates a comprehensive understanding of potential underlying factors and the implementation of specialized treatment strategies.
Potential Causes and Contributing Factors
Several factors may contribute to the persistence of intractable eczema:
- Genetic Predisposition: Mutations in genes responsible for skin barrier function can increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to allergens, pollutants, or irritants may exacerbate symptoms.
- Immune System Dysregulation: An overactive immune response can perpetuate inflammation.
- Psychological Stress: Emotional stress has been linked to the exacerbation of eczema symptoms.
Challenges in Management
Managing intractable eczema presents unique challenges:
- Identifying Triggers: Determining specific allergens or irritants can be complex.
- Treatment Resistance: Standard therapies may lose effectiveness over time.
- Psychosocial Impact: Chronic symptoms can lead to emotional distress and social withdrawal.
Advanced Treatment Strategies
For patients with intractable eczema, the following advanced treatments may be considered:
1. Biologic Therapies
Biologics, such as dupilumab, target specific immune pathways involved in eczema. Clinical cases have demonstrated significant improvement in patients unresponsive to conventional treatments.
2. Phototherapy
Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can reduce inflammation and itching, offering relief for some patients.
3. Systemic Immunosuppressants
Medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed to suppress the immune response, though they require careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
4. Psychotherapy
Addressing psychological factors through therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy can improve coping mechanisms and potentially reduce symptom severity. PubMed
Comprehensive Management Approach
An effective management plan for intractable eczema should be multidisciplinary, encompassing:
- Skincare Regimen: Regular use of emollients and gentle cleansers to maintain skin hydration.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and minimizing exposure to known allergens or irritants.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating stress-reduction techniques and a balanced diet to support overall health.
Intractable eczema poses significant challenges, but advancements in treatment options offer hope for improved management. A personalized, comprehensive approach addressing both physiological and psychological aspects is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.