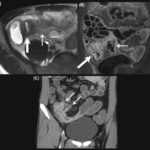
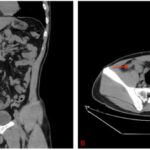
An intra-abdominal abscess is a localized collection of pus within the abdominal cavity, often resulting from an intra-abdominal infection or a perforation of the gastrointestinal tract. These abscesses can involve any intra-abdominal organ or be located freely within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, including in between loops of bowel.
Pathophysiology
Intra-abdominal abscesses commonly occur as complications of intra-abdominal infections, such as diverticulitis, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, pelvic inflammatory disease, or following abdominal surgery, gastrointestinal tract perforation, or penetrating abdominal trauma. Abscesses confined to single organs or structures can also occur, such as in the liver, spleen, subphrenic area, or psoas muscle.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with intra-abdominal abscesses often present with abdominal pain, fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, and leukocytosis. A palpable abdominal mass, peritoneal findings, ileus, and anorexia may also be present. The presentation can range from mild abdominal pain and fever to fulminant septic shock.
Diagnostic Evaluation
The diagnosis of an intra-abdominal abscess is confirmed by radiologic studies such as ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scan. CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis is often more reliable and provides better delineation of anatomic location and size of the abscess. Laboratory testing is not specific; a complete blood count (CBC) showing a leukocytosis greater than 20,000 or a left shift can point towards abscess formation; however, a normal white blood cell (WBC) count or lack of fever does not exclude the diagnosis.
Management
Treatment involves adequate source control (abscess drainage, whether percutaneous or surgical) as well as early appropriate and effective antimicrobial therapy. If untreated, an intra-abdominal abscess may lead to clinical deterioration, including sepsis or septic shock.
Intra-abdominal abscesses are serious medical conditions that require prompt diagnosis and management. Early recognition and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent severe complications and improve patient outcomes.