Infectious joint disorders, also known as septic arthritis, are serious conditions caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections that infiltrate the joints. Immediate diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term damage and disability.
Causes of Infectious Joint Disorders
Infectious arthritis occurs when pathogens enter the joint through various routes. The primary causes include:
- Bacterial Infections: Staphylococcus aureus is the most common bacterial cause, often entering through wounds or surgical procedures.
- Viral Infections: Certain viruses, such as hepatitis B, HIV, and parvovirus B19, can lead to joint inflammation.
- Fungal Infections: Candida and Aspergillus species are known to cause joint infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Injury and Surgery: Open fractures, invasive procedures, or prosthetic implants increase the risk of infection.
Symptoms of Infectious Joint Disorders
Common symptoms include:
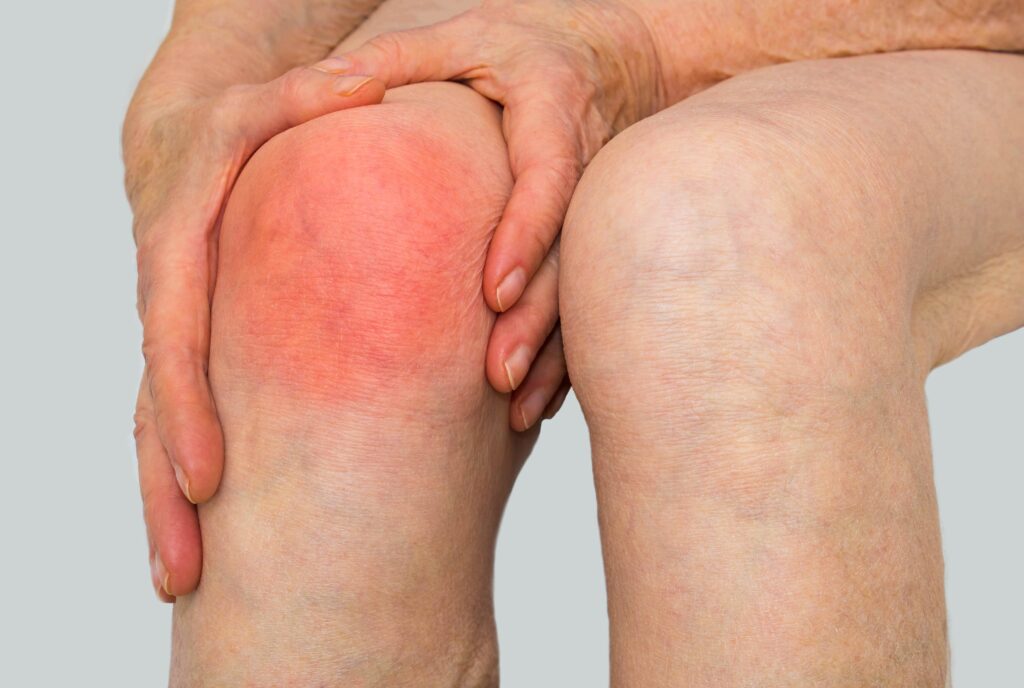
- Severe joint pain
- Swelling and warmth around the affected area
- Restricted movement and stiffness
- Fever and chills
- Redness and tenderness near the infected joint
Risk Factors for Infectious Arthritis
Certain individuals are more prone to developing infectious joint disorders, including:
- People with weakened immune systems
- Individuals with diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis
- Patients using corticosteroids or undergoing chemotherapy
- Those with joint prosthetics or recent joint surgeries
Diagnosis of Infectious Joint Disorders
Effective diagnosis involves a combination of the following methods:
- Joint Aspiration: Extraction and analysis of synovial fluid to identify pathogens.
- Blood Tests: Elevated white blood cell count and inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) indicate infection.
- Imaging Techniques: X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI scans help visualize joint damage.
Treatment Options for Infectious Joint Disorders
Treatment strategies aim to eradicate the infection while preserving joint function. Key approaches include:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Administered intravenously to combat bacterial infections effectively.
- Antifungal and Antiviral Medications: Tailored to address fungal or viral infections.
- Joint Drainage: Surgical procedures like arthroscopy or open drainage may be necessary to remove infected fluid.
- Physical Therapy: Helps restore joint mobility and prevent stiffness.
Prevention of Infectious Joint Disorders
Preventive measures include:
- Maintaining good hygiene during surgical procedures
- Timely treatment of skin wounds and infections
- Regular medical checkups for individuals with joint prosthetics
- Vaccinations for high-risk individuals
Prognosis and Recovery
With prompt treatment, most patients recover fully without permanent joint damage. However, delayed intervention may result in joint deformity, reduced mobility, or chronic pain.
FAQs
Q1: What are the early signs of infectious arthritis?
A1: Early signs include sudden joint pain, swelling, and fever. Seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Q2: Can infectious arthritis be prevented?
A2: Practicing good hygiene, treating infections promptly, and taking preventive measures during surgery can reduce the risk.
Q3: How long does recovery take?
A3: Recovery time varies depending on the severity but generally ranges from a few weeks to several months with proper treatment.
Q4: Is infectious arthritis contagious?
A4: No, infectious arthritis itself is not contagious, but the pathogens that cause it may be transmissible.
Q5: Which joints are most commonly affected?
A5: The knee, hip, and shoulder joints are commonly affected, though any joint can develop an infection.