Infant botulism is a rare but serious illness caused by the ingestion of Clostridium botulinum spores, which produce a powerful neurotoxin in the baby’s intestines. This condition primarily affects infants under 12 months of age due to their immature digestive systems.
Causes of Infant Botulism
The primary cause of infant botulism is the ingestion of C. botulinum spores. These spores can be found in various sources, including:
- Honey: The most well-known source; never feed honey to infants under one year old.
- Soil and Dust: Spores are naturally present in the environment and can enter through breathing or hand-to-mouth contact.
- Contaminated Food or Surfaces: Improperly cleaned bottles, pacifiers, or feeding equipment may harbor spores.
Symptoms of Infant Botulism
Recognizing the early signs of infant botulism is crucial for prompt treatment. Symptoms often appear gradually and may include:
- Constipation: One of the earliest and most common signs.
- Weak Cry: Babies may sound softer or weaker than usual.
- Poor Feeding: Difficulty sucking or swallowing.
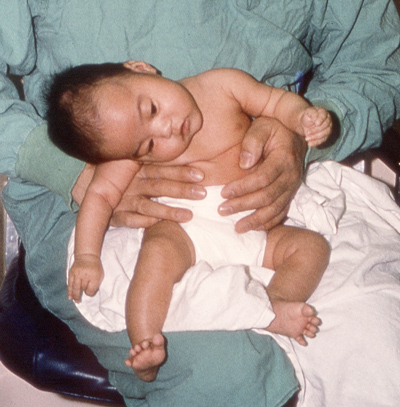
- Floppiness (Hypotonia): Muscle weakness causing reduced movement.
- Drooping Eyelids: Due to muscle paralysis.
- Breathing Problems: In severe cases, respiratory distress may occur.
Diagnosis of Infant Botulism
Healthcare providers diagnose infant botulism based on:
- Medical History: Reviewing recent food intake and environmental exposure.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs like weak muscles and poor reflexes.
- Stool Sample Testing: Lab tests to detect C. botulinum toxin or spores in the baby’s feces.
Treatment for Infant Botulism
Early intervention is essential. Treatment options typically include:
- Botulism Immune Globulin Intravenous (BIG-IV): A specialized antitoxin that neutralizes the botulinum toxin, reducing recovery time.
- Supportive Care: Includes mechanical ventilation, intravenous fluids, and nutritional support in severe cases.
- Hospitalization: Most infants require hospitalization for monitoring and care until full recovery.
Prevention of Infant Botulism
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of infant botulism. Key strategies include:
- Avoid Honey: Never feed honey to infants under 12 months.
- Maintain Clean Environments: Regularly clean feeding equipment, pacifiers, and toys.
- Proper Food Handling: Follow safe preparation and storage practices for infant food.
Complications of Infant Botulism
While most infants recover fully with proper treatment, complications may arise, including:
- Respiratory Distress: In severe cases, respiratory support may be necessary.
- Delayed Development: Muscle weakness may temporarily affect motor skill milestones.
- Feeding Challenges: Some infants may experience prolonged feeding difficulties.
Recovery and Prognosis
With prompt treatment, most infants make a full recovery. The recovery process can take several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the condition. Follow-up care may involve physical therapy to rebuild muscle strength and coordination.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: Can infant botulism be contagious?
No, infant botulism is not contagious. It occurs due to ingestion of spores, not person-to-person contact.
Q2: How long does recovery take for infant botulism?
Recovery may take weeks to months, depending on the severity of symptoms and the timeliness of treatment.
Q3: Are probiotics effective in preventing infant botulism?
While probiotics support gut health, they are not proven to prevent infant botulism.
Q4: Can infant botulism recur?
Recurrence is rare but possible if new exposure to C. botulinum spores occurs.
Q5: Is there a vaccine for infant botulism?
Currently, no vaccine exists specifically for infant botulism; prevention focuses on reducing exposure.