Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (IST) is a condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate originating from the sinus node without an identifiable cause. Unlike physiological tachycardia, which occurs as a normal response to exercise, stress, or illness, IST presents as a persistent and exaggerated increase in heart rate even at rest or with minimal exertion.
Symptoms of Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia
Individuals with IST may experience the following symptoms:
- Palpitations (rapid or irregular heartbeat)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Anxiety or feelings of unease
- Exercise intolerance
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of IST is not always clear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction: Overactive sympathetic nervous system responses may lead to increased heart rate.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Elevated catecholamine levels can trigger sinus tachycardia.
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS): IST may overlap with POTS in some patients.
- Medications or Stimulants: Certain drugs, caffeine, and energy supplements can contribute to IST.
Diagnosis of IST
Diagnosing IST involves ruling out other potential causes of tachycardia. Diagnostic steps include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Identifies heart rhythm and confirms sinus tachycardia.
- Holter Monitor or Event Recorder: Provides continuous heart rate monitoring.
- Tilt Table Test: Assesses autonomic function in cases with suspected nervous system involvement.
- Blood Tests: Evaluates thyroid function, electrolyte balance, and hormonal levels.
Treatment Options for IST
Treatment for IST focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Options include:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Reducing caffeine and stimulant intake
- Managing stress through mindfulness techniques
- Practicing regular, low-intensity exercise to stabilize heart rate
2. Medications
- Beta-Blockers: Effective in lowering heart rate and controlling symptoms
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Helps regulate heart rate
- Ivabradine: Specifically designed to reduce sinus node firing rates
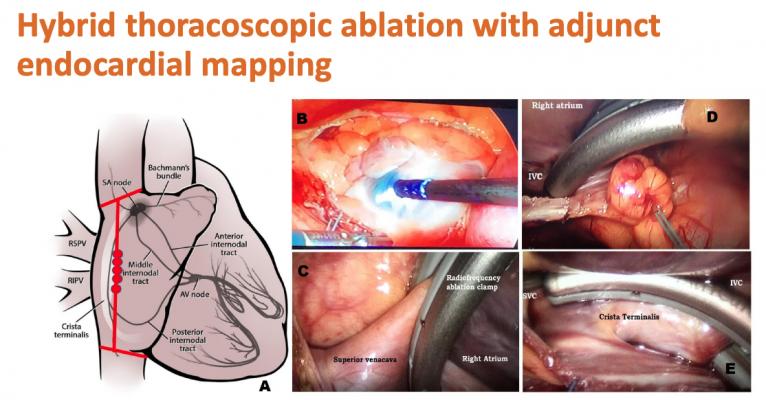
3. Catheter Ablation
- Reserved for severe cases resistant to medical therapy
- Targets the sinus node to modify electrical signals causing tachycardia
4. Psychological Support
Since anxiety often worsens IST symptoms, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or counseling may be beneficial.
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for IST varies. While some individuals experience mild symptoms that improve with lifestyle changes, others may require long-term medical management. IST is generally non-life-threatening but may significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being.
Preventive Measures
Although IST cannot always be prevented, patients may reduce their risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Avoiding stimulants and excessive caffeine
- Managing stress effectively
IST vs. Other Forms of Tachycardia
IST can be distinguished from other types of tachycardia through specific ECG patterns, symptom presentation, and triggers. Key differences include:
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can IST be cured completely?
A: While IST may not always be completely cured, symptoms can often be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, medications, or procedures like catheter ablation.
Q2: Is IST dangerous or life-threatening?
A: IST is generally not life-threatening but can significantly impact quality of life if left untreated.
Q3: What lifestyle changes help manage IST?
A: Reducing caffeine, managing stress, improving sleep quality, and maintaining hydration are key strategies for IST management.
Q4: Can anxiety trigger IST?
A: Yes, anxiety can worsen IST symptoms. Managing mental health through relaxation techniques can help.
Q5: Is IST related to heart disease?
A: IST itself is not considered a form of structural heart disease, but its symptoms may mimic those of other heart conditions.