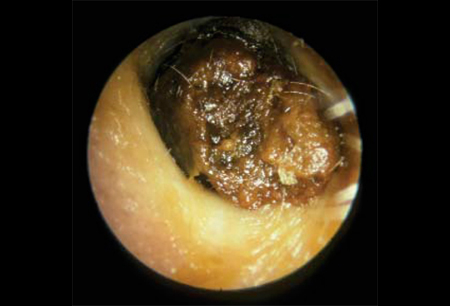
Impacted cerumen refers to a condition in which earwax accumulates in the ear canal to the point that it causes discomfort, hearing loss, or other symptoms. Earwax, medically known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal to protect the ear from dust, debris, and infection. When excess wax builds up, it may harden and obstruct the ear canal.
Causes of Impacted Cerumen
Several factors can contribute to impacted earwax, including:
- Excessive Wax Production: Some individuals naturally produce more earwax than others.
- Narrow or Curved Ear Canals: Anatomical features can hinder the natural expulsion of wax.
- Use of Earbuds or Hearing Aids: Devices worn inside the ear can push wax deeper.
- Inappropriate Cleaning Methods: Cotton swabs or hairpins may compact the wax instead of removing it.
- Aging: Older adults may experience drier wax, making impaction more likely.
Symptoms of Impacted Cerumen
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the blockage. Common signs include:
- Hearing Loss: Partial or complete hearing reduction.
- Earache: Pain or discomfort in the affected ear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sounds.
- Ear Fullness: A sensation of pressure or blockage.
- Dizziness or Vertigo: Balance issues may arise in severe cases.
- Itching or Odor: A foul smell may indicate an infection due to trapped bacteria.
Diagnosis of Impacted Cerumen
Healthcare providers diagnose impacted cerumen through:
- Otoscopy: A visual inspection of the ear canal using an otoscope.
- Audiometry Tests: Conducted if hearing impairment is suspected.
Treatment Options for Impacted Cerumen
Effective treatment methods include:
1. Ear Drops
- Over-the-counter solutions containing hydrogen peroxide, mineral oil, or saline can soften wax, promoting its natural expulsion.
2. Irrigation (Ear Syringing)
- A healthcare provider may flush the ear canal with warm saline or water to dislodge wax.
3. Manual Removal
- ENT specialists often use tools such as suction devices, curettes, or forceps to extract hardened wax safely.
4. Microsuction
- This precise technique employs a suction device for effective removal without water.
Prevention of Impacted Cerumen
To reduce the risk of earwax buildup:
- Avoid Cotton Swabs: These tend to push wax deeper.
- Use Earwax Softening Drops: Regular use can prevent hardened wax.
- Keep Ears Dry: Moisture promotes wax accumulation.
- Routine Checkups: Regular examination by an ENT specialist can help monitor wax buildup.
Complications of Untreated Impacted Cerumen
If left untreated, impacted cerumen may lead to:
- Hearing Impairment: Prolonged blockage can damage the eardrum.
- Infections: Trapped bacteria may cause otitis externa (outer ear infection).
- Chronic Tinnitus: Persistent ringing in the ear can develop.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent hearing loss
- Severe ear pain or discomfort
- Unrelieved symptoms after home treatment
Impacted cerumen is a common yet manageable condition. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent complications. For individuals prone to excessive wax buildup, adopting preventive measures and scheduling regular checkups are key to maintaining ear health.