Idiopathic Parkinsonism is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms. Unlike secondary parkinsonism, its cause is unknown, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
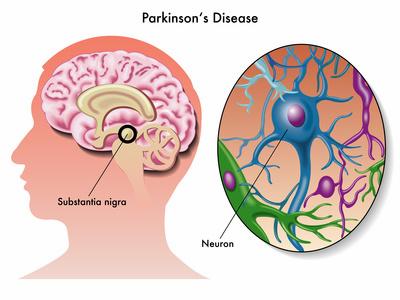
Causes of Idiopathic Parkinsonism
While the exact cause remains unclear, research suggests that genetic and environmental factors contribute to idiopathic parkinsonism. Key risk factors include:
- Age: Incidence increases significantly with age, especially after 60.
- Genetics: Mutations in genes like SNCA, LRRK2, and PARK2 are linked to familial cases.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and certain toxins may elevate risk.
- Oxidative Stress: Imbalance in free radicals can lead to neuronal damage.
Symptoms of Idiopathic Parkinsonism
Symptoms typically progress gradually and vary in intensity. They can be classified into motor and non-motor categories:
Motor Symptoms
- Tremors: Often begin in the hands and worsen with rest.
- Bradykinesia: Slowed movement that affects everyday activities.
- Muscle Rigidity: Stiffness that reduces flexibility and causes discomfort.
- Postural Instability: Impaired balance leading to frequent falls.
Non-Motor Symptoms
- Cognitive Decline: Memory issues and reduced mental sharpness.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia, vivid dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Blood pressure changes, bladder control issues, and excessive sweating.
- Emotional Changes: Depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
Diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinsonism
Diagnosing idiopathic parkinsonism requires clinical evaluation and medical history analysis. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Neurological Examination: Assessing motor function, reflexes, and gait.
- DaTscan Imaging: Identifies dopamine transporter deficiencies in the brain.
- MRI and CT Scans: Rule out other conditions like stroke or brain tumors.
- Response to Levodopa: Improvement after medication often confirms Parkinson’s diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Idiopathic Parkinsonism
Though there is no cure, various treatments can manage symptoms effectively:
Medications
- Levodopa-Carbidopa: Primary treatment that restores dopamine levels.
- Dopamine Agonists: Mimic dopamine effects in the brain.
- MAO-B Inhibitors: Slow dopamine breakdown, improving symptom control.
- Anticholinergics: Help reduce tremors and muscle stiffness.
Surgical Interventions
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrodes implanted in the brain improve motor control.
- Pallidotomy and Thalamotomy: Targeted surgical techniques that reduce severe tremors and rigidity.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Physical Therapy: Enhances mobility, balance, and flexibility.
- Speech Therapy: Helps improve speech and swallowing functions.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists with adapting to daily tasks and improving quality of life.
Prognosis and Management
While idiopathic parkinsonism is progressive, early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can significantly enhance quality of life. Support groups, counseling, and social engagement play vital roles in improving emotional well-being.
FAQs
What is the main difference between idiopathic and secondary parkinsonism?
Idiopathic parkinsonism arises without a known cause, whereas secondary parkinsonism results from identifiable factors like medications, brain injuries, or toxins.
How long can someone live with idiopathic parkinsonism?
With proper treatment, individuals may live for decades post-diagnosis. Life expectancy varies based on symptom severity and overall health.
Are there any preventive measures for idiopathic parkinsonism?
While prevention is uncertain, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and reducing toxin exposure may lower risk.
Can idiopathic parkinsonism be misdiagnosed?
Yes, conditions such as essential tremor, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy may mimic idiopathic parkinsonism symptoms, leading to misdiagnosis.
What are the latest advancements in treating idiopathic parkinsonism?
Innovative therapies, including gene-targeted treatments, stem cell research, and improved DBS technology, show promising results in symptom management.
Idiopathic Parkinsonism remains a complex condition requiring multidisciplinary care. Advances in medical research continue to improve treatment outcomes and enhance patient well-being. Early diagnosis and proactive management are essential for maintaining quality of life.