Idiopathic neutropenia is a rare hematological disorder characterized by an unexplained decrease in neutrophil count. Neutrophils are vital white blood cells responsible for fighting infections. This condition can manifest in both children and adults, with varying degrees of severity.
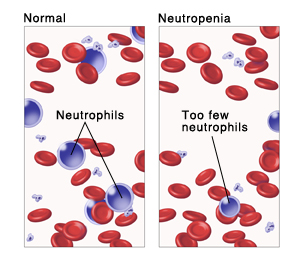
What is Idiopathic Neutropenia?
Idiopathic neutropenia is diagnosed when no identifiable cause for the neutrophil deficiency is found. The term “idiopathic” indicates that the origin is unknown, and patients often undergo extensive evaluation to rule out secondary causes such as medications, autoimmune disorders, or infections.
Types of Idiopathic Neutropenia
- Chronic Idiopathic Neutropenia (CIN): Persistent low neutrophil counts lasting longer than six months without a known cause.
- Acute Idiopathic Neutropenia: Sudden onset with rapid resolution or progression.
Causes and Risk Factors
Although the exact cause remains unknown, potential contributing factors include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Bone marrow suppression
- Autoimmune activity
- Environmental factors
Symptoms of Idiopathic Neutropenia
Symptoms may vary based on the severity of neutropenia. Common signs include:
- Frequent bacterial infections
- Fever and chills
- Mouth ulcers
- Sore throat
- Skin abscesses
- Respiratory tract infections
Diagnosis and Evaluation
The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Determines the neutrophil count.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Identifies bone marrow abnormalities.
- Autoimmune Screening: Rules out immune-related causes.
- Genetic Testing: Assesses inherited neutrophil disorders.
Treatment Options
Treatment strategies are based on severity:
- Mild Cases: Often require observation without intervention.
- Moderate Cases: May involve prophylactic antibiotics and close monitoring.
- Severe Cases: Require aggressive treatments such as:
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
- Immunosuppressive therapy
- Bone marrow transplantation
Lifestyle and Management
Individuals with idiopathic neutropenia should adopt the following practices:
- Maintain good hygiene to reduce infection risks.
- Avoid contact with sick individuals.
- Follow a balanced diet to support immune function.
- Adhere to vaccination schedules as advised by healthcare providers.
Potential Complications
If untreated, idiopathic neutropenia can lead to:
- Recurring infections
- Severe septicemia
- Delayed wound healing
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for idiopathic neutropenia depends on its severity and response to treatment. Many patients with mild cases lead normal lives with minimal interventions. Severe cases may require long-term medical care and follow-up.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the difference between neutropenia and idiopathic neutropenia?
Neutropenia is a broad term for low neutrophil counts, while idiopathic neutropenia is a subtype where no specific cause is identified.
Can idiopathic neutropenia be cured?
There is no definitive cure, but treatments can manage symptoms effectively.
Is idiopathic neutropenia life-threatening?
Mild cases are typically harmless, but severe forms can increase susceptibility to serious infections.
Can children develop idiopathic neutropenia?
Yes, idiopathic neutropenia can affect children, though it often resolves without intervention.
What lifestyle changes can help manage idiopathic neutropenia?
Maintaining hygiene, reducing exposure to infectious agents, and following medical advice can significantly reduce risks.
Idiopathic neutropenia is a complex condition that requires careful diagnosis and management. While mild cases may resolve without medical intervention, severe instances demand targeted treatments to prevent complications. Individuals experiencing persistent infections or other neutropenia-related symptoms should consult healthcare professionals promptly.