Idiopathic hypersomnia (IH) is a rare and chronic neurological sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) despite adequate or prolonged nighttime sleep. Unlike other sleep disorders, IH is not linked to disrupted sleep patterns or insufficient rest. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management.
What Causes Idiopathic Hypersomnia?
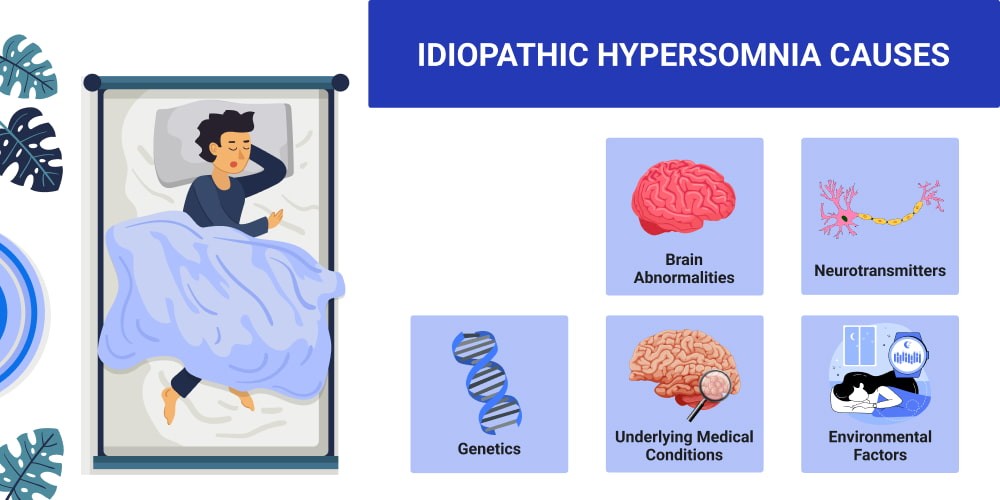
The exact cause of idiopathic hypersomnia remains unknown, but research suggests it may involve an imbalance in brain chemicals responsible for regulating sleep and wakefulness. Possible contributing factors include:
- Neurochemical Imbalance: Abnormalities in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) signaling.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of hypersomnia may increase risk.
- Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction: Disruptions in body functions like blood pressure and heart rate.
Key Symptoms of Idiopathic Hypersomnia
Individuals with idiopathic hypersomnia may experience the following symptoms:
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness (EDS): Persistent drowsiness despite adequate sleep.
- Unrefreshing Sleep: Sleep that feels non-restorative even after extended hours.
- Sleep Inertia (Sleep Drunkenness): Prolonged difficulty in waking up, often accompanied by confusion.
- Cognitive Impairment: Trouble with memory, focus, and mental clarity.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, or low blood pressure.
Diagnosing Idiopathic Hypersomnia
Diagnosing IH requires a thorough evaluation to rule out other sleep disorders such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea. The diagnostic process may involve:
- Detailed Medical History: Reviewing sleep patterns and daytime alertness.
- Polysomnography (PSG): An overnight sleep study to analyze sleep stages and cycles.
- Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): A daytime nap test to assess how quickly a person falls asleep.
- Actigraphy: A wearable device that tracks movement and sleep-wake patterns.
Treatment Options for Idiopathic Hypersomnia
While there is no definitive cure for IH, various treatment strategies can help manage symptoms:
Medications
- Stimulants: Such as modafinil or armodafinil to promote wakefulness.
- Sodium Oxybate: May improve nighttime sleep quality and reduce daytime drowsiness.
- Melatonin or Hypnotics: To regulate sleep patterns and enhance restfulness.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining consistent sleep schedules and creating a restful sleep environment.
- Dietary Changes: Balanced nutrition to support overall energy levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to improve wakefulness and overall health.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT techniques can help manage associated anxiety, depression, or emotional stress resulting from chronic fatigue.
Coping Strategies for Idiopathic Hypersomnia
Individuals with IH can adopt various techniques to improve their quality of life:
- Workplace Adjustments: Flexible schedules or remote work options may help accommodate fatigue.
- Scheduled Naps: Short, strategic naps can provide temporary relief from drowsiness.
- Support Networks: Joining IH support groups can provide emotional encouragement and shared strategies.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
Idiopathic hypersomnia is a lifelong condition, but symptoms can often be managed effectively through a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle modifications. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure optimal treatment adjustments.
FAQs:
What triggers idiopathic hypersomnia?
Idiopathic hypersomnia is not triggered by specific factors, but stress, irregular sleep, and certain medications may exacerbate symptoms.
Is idiopathic hypersomnia the same as narcolepsy?
No. While both involve excessive daytime sleepiness, narcolepsy often includes sudden sleep attacks, cataplexy, and REM sleep disturbances.
Can idiopathic hypersomnia improve over time?
Some individuals may experience symptom improvements with proper treatment, though complete recovery is rare.
What is the best treatment for idiopathic hypersomnia?
A combination of medications like modafinil, improved sleep hygiene, and lifestyle changes is considered the most effective approach.
Is idiopathic hypersomnia considered a disability?
Yes, idiopathic hypersomnia can qualify as a disability if it significantly impairs daily activities.
Idiopathic hypersomnia presents unique challenges that require a comprehensive understanding for effective management. By combining medical treatments with lifestyle strategies, individuals with IH can improve their quality of life and achieve better control over their symptoms.