Hypokalemia refers to a medical condition characterized by abnormally low potassium levels in the bloodstream. Potassium is a crucial electrolyte that supports various bodily functions, including muscle contractions, nerve signals, and heart rhythms.
Causes of Hypokalemia
Dietary Deficiencies
- Insufficient potassium intake from food sources.
- Poor dietary habits or restrictive diets can elevate risk.
Medical Conditions
- Chronic kidney disease.
- Excessive vomiting or diarrhea.
- Certain medications such as diuretics or laxatives.
Lifestyle Factors
- Intense physical activity leading to excessive sweating.
- Alcohol abuse or extreme dehydration.
Symptoms of Hypokalemia
- Muscle weakness and fatigue.
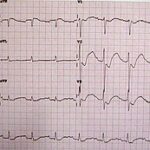
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).
- Cramps and spasms.
- Numbness or tingling sensations.
- Digestive issues like bloating or constipation.
Strategies for Hypokalemia Prevention
1. Balanced Diet with Potassium-Rich Foods
Incorporating potassium-rich foods into daily meals is a crucial preventive measure. Some excellent sources include:
- Bananas
- Oranges
- Spinach
- Avocados
- Sweet Potatoes
- Tomatoes
2. Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
- Maintain adequate fluid intake.
- Use electrolyte-enhanced drinks during strenuous exercise or heat exposure.
3. Medication Management
- Consult healthcare providers before starting or adjusting diuretics or laxatives.
- Potassium supplements may be recommended in some cases.
4. Managing Chronic Conditions
- For individuals with chronic kidney disease or other related health issues, consistent medical supervision is vital.
5. Regular Health Monitoring
- Periodic blood tests can help track potassium levels.
- People on medications that affect potassium should monitor levels more frequently.
Potassium-Rich Meal Plan for Hypokalemia Prevention
| Meal Time | Food Suggestions |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Avocado toast with spinach and tomatoes |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon with a sweet potato side |
| Snack | Banana with Greek yogurt |
| Dinner | Stir-fry with chicken, bell peppers, and beans |
Exercise and Potassium Balance
Physical activity increases potassium demand. Follow these tips:
- Stretch before workouts to reduce muscle fatigue.
- Drink potassium-enriched beverages during prolonged exercise.
Recommended Daily Potassium Intake
The recommended daily potassium intake varies by age and lifestyle:
- Adults: 2,500 to 3,400 mg/day.
- Pregnant/Breastfeeding Women: 2,900 to 3,400 mg/day.
- Children (4-8 years): 2,300 mg/day.
Potential Complications of Untreated Hypokalemia
- Severe muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis).
- Life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Respiratory failure in extreme cases.
Preventing hypokalemia requires a proactive approach involving dietary adjustments, proper hydration, medication management, and regular health monitoring. By adopting these preventive strategies, individuals can maintain healthy potassium levels and safeguard their overall well-being.