Hypoestrogenism refers to a medical condition characterized by abnormally low levels of estrogen in the body. Estrogen is a crucial hormone that plays a vital role in regulating various physiological functions, particularly in women. Its deficiency can result in several health complications.
Causes of Hypoestrogenism
Hypoestrogenism can occur due to several factors, including:
- Natural Causes: Menopause, perimenopause, and aging significantly reduce estrogen production.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as Turner syndrome, primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can impair estrogen levels.
- Lifestyle Factors: Extreme exercise, eating disorders, and chronic stress may suppress estrogen production.
- Medications and Treatments: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or hormonal medications can reduce estrogen.
- Surgical Interventions: Oophorectomy (removal of ovaries) directly causes hypoestrogenism.
Symptoms of Hypoestrogenism
The symptoms can vary but often include:
- Menstrual Irregularities: Irregular or absent periods
- Vaginal Dryness: Leading to discomfort during intercourse
- Hot Flashes and Night Sweats: Common in menopause-related hypoestrogenism
- Mood Changes: Anxiety, depression, and irritability
- Bone Health Issues: Osteoporosis and increased fracture risk
- Skin and Hair Changes: Dry skin, thinning hair, and brittle nails
Diagnosing Hypoestrogenism
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History Assessment: Identifying potential risk factors or symptoms.
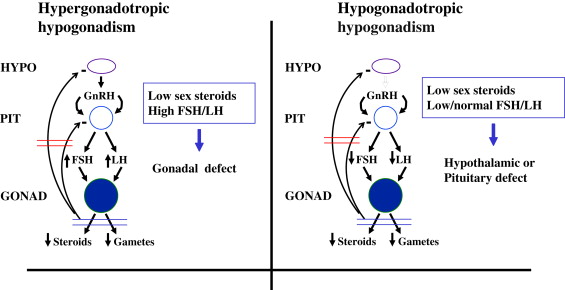
- Blood Tests: Measuring estradiol, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess ovarian function or identify underlying issues.
Treatment Options for Hypoestrogenism
Treatment strategies are based on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms:
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- Estrogen-Only Therapy: For individuals who have undergone a hysterectomy.
- Combined HRT: For women with an intact uterus to reduce endometrial cancer risk.
Medications
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Such as raloxifene to improve bone density.
- Vaginal Estrogen Products: To alleviate vaginal dryness and related symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
- Balanced Diet: Including calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
- Regular Exercise: To strengthen bones and improve overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress to support hormonal balance.
Complications Associated with Hypoestrogenism
Without treatment, hypoestrogenism can lead to severe health concerns, including:
- Osteoporosis: Increased risk of fractures and bone loss.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Greater risk of heart disease.
- Infertility: Due to disrupted ovulation cycles.
Preventive Measures
Preventive strategies to reduce the risk of hypoestrogenism include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Avoid extreme dieting or over-exercising.
- Routine Health Screenings: Early diagnosis and intervention can minimize risks.
- Hormone Monitoring: Regular check-ups for women approaching menopause.
Understanding the Estrogen Pathway in the Body
Below is a visual representation of the estrogen production process in the human body:
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the main cause of hypoestrogenism?
The most common cause is menopause, but it can also result from certain medical conditions, lifestyle factors, or surgeries.
Q2. Can hypoestrogenism be treated naturally?
In mild cases, dietary changes, stress reduction, and herbal supplements may help balance estrogen levels.
Q3. How does hypoestrogenism affect fertility?
Estrogen deficiency can disrupt ovulation, reducing the chances of conception.
Q4. What foods are recommended for boosting estrogen?
Foods such as flaxseeds, soy products, and leafy greens are known to support estrogen levels.
Q5. Is hormone replacement therapy safe?
HRT is generally safe when prescribed correctly; however, it’s important to discuss risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.