Hypertriglyceridemia refers to an elevated level of triglycerides in the blood, a condition linked to increased cardiovascular risks. Triglycerides are a type of fat derived from excess calories stored in the body. Maintaining balanced triglyceride levels is crucial for overall health.
Causes of Hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia can result from various factors, including:
Primary Causes (Genetic)
- Familial combined hyperlipidemia
- Familial hypertriglyceridemia
- Lipoprotein lipase deficiency
Secondary Causes (Lifestyle & Medical Conditions)
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Uncontrolled diabetes
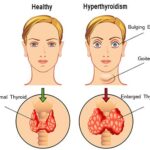
- Hypothyroidism
- Chronic kidney disease
- Alcohol consumption
- High carbohydrate diets
- Certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids, beta-blockers)
Symptoms of Hypertriglyceridemia
Mild cases often present no symptoms. However, severely elevated triglycerides can lead to:
- Abdominal pain
- Pancreatitis
- Fatty liver disease
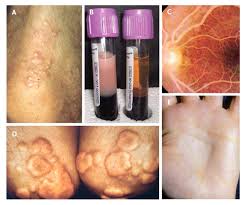
- Eruptive xanthomas (yellowish skin lesions)
Diagnosis of Hypertriglyceridemia
Healthcare providers assess triglyceride levels through a fasting lipid profile test. According to the American Heart Association (AHA):
- Normal: <150 mg/dL
- Borderline-high: 150-199 mg/dL
- High: 200-499 mg/dL
- Very high: ≥500 mg/dL
Risk Factors for Hypertriglyceridemia
Key risk factors include:
- Family history of lipid disorders
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High-fat, sugar-rich diets
- Insulin resistance and diabetes
- Smoking and excessive alcohol intake
Health Complications Associated with Hypertriglyceridemia
If untreated, hypertriglyceridemia may result in severe conditions such as:
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
- Atherosclerosis
- Pancreatitis
- Stroke
Treatment and Management of Hypertriglyceridemia
Effective management involves lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Reduce saturated fats, trans fats, and refined carbohydrates
- Increase intake of omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseeds)
- Embrace a Mediterranean diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats
- Weight Management:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight
- Exercise:
- Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly
- Limiting Alcohol and Sugar Intake:
- Minimizing sugary drinks, sweets, and alcohol consumption
Medications
In severe cases, medications may be necessary:
- Statins: Effective for reducing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides
- Fibrates: Best suited for triglyceride-specific lowering
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): Reduces both LDL and triglyceride levels
- Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements: Recommended for managing high triglyceride levels
Prevention Strategies
- Adopting a balanced diet with healthy fats
- Staying physically active
- Regular screening for lipid profile, especially if at risk
- Managing underlying conditions like diabetes and obesity
Hypertriglyceridemia is a significant health concern that can elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease and other serious conditions. Early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical treatments can effectively manage this condition. Regular health check-ups and preventive measures are key to ensuring optimal lipid levels and overall well-being.