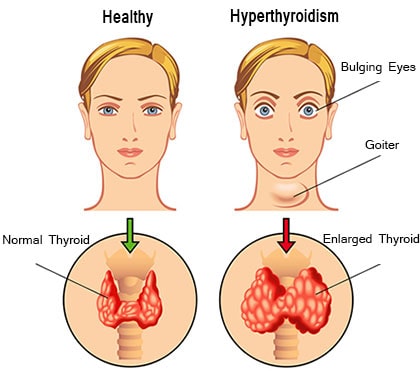
Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland that produces excessive thyroid hormones. These hormones regulate metabolism, and their excess can significantly impact the body’s functions.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Several factors may contribute to hyperthyroidism, including:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder that prompts the thyroid to overproduce hormones.
- Thyroid Nodules: Benign lumps within the thyroid gland that may become overactive.
- Excess Iodine Intake: High iodine levels from certain medications or supplements can stimulate excess hormone production.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland, which may release stored hormones rapidly.
- Pituitary Tumors: Rarely, tumors in the pituitary gland may influence hormone overproduction.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Common symptoms include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- Tremors in hands and fingers
- Increased appetite
- Sweating and heat intolerance
- Frequent bowel movements
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Insomnia
- Menstrual cycle changes
- Enlarged thyroid (goiter)
Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Blood Tests: TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) levels are checked, along with T3 and T4 hormone levels.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: Measures thyroid iodine absorption.
- Thyroid Scan: Visualizes the gland’s structure and activity.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Identifies thyroid nodules and gland enlargement.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Treatment depends on the condition’s cause and severity:
1. Antithyroid Medications
- Methimazole and Propylthiouracil (PTU) are commonly prescribed to inhibit hormone production.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
- This treatment reduces thyroid gland activity by shrinking it gradually.
3. Beta-Blockers
- Medications like Propranolol help manage rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and tremors by controlling symptoms.
4. Thyroid Surgery
- Partial or total thyroidectomy may be recommended for severe cases or when other treatments prove ineffective.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To manage hyperthyroidism effectively:
- Follow a balanced diet low in iodine.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and stress triggers.
- Maintain a healthy sleep schedule.
- Regular exercise may help regulate metabolism.
Complications of Hyperthyroidism
If untreated, hyperthyroidism may lead to:
- Thyroid Storm: A life-threatening condition marked by fever, confusion, and severe heart issues.
- Osteoporosis: Excess thyroid hormones weaken bones over time.
- Heart Problems: Increased risk of arrhythmias, high blood pressure, and heart failure.
Preventing Hyperthyroidism
While some causes are unavoidable, preventive measures may include:
- Regular thyroid check-ups
- Balanced iodine intake
- Managing stress and maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Hyperthyroidism vs. Hypothyroidism
| Feature | Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid Activity | Overactive | Underactive |
| Symptoms | Weight loss, rapid heartbeat | Weight gain, fatigue |
| Common Cause | Graves’ disease | Hashimoto’s thyroiditis |
| Treatment | Medications, RAI therapy | Hormone replacement therapy |
FAQs
1. Can stress cause hyperthyroidism?
Stress alone doesn’t cause hyperthyroidism, but it can worsen symptoms and trigger flare-ups in those with existing conditions.
2. Is hyperthyroidism curable?
Yes, with appropriate treatment such as medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery, hyperthyroidism can be effectively managed or even cured.
3. Can diet influence hyperthyroidism?
Yes, reducing iodine-rich foods like seafood and iodized salt may help manage hyperthyroidism symptoms.
4. Are there natural remedies for hyperthyroidism?
Some herbs like bugleweed and lemon balm may support hormone balance, but consult your doctor before starting any alternative treatments.
5. How long does hyperthyroidism treatment last?
Treatment duration varies, with some requiring lifelong medication, while others may achieve remission after several months.
Hyperthyroidism is a manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated effectively. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions to maintain their well-being.