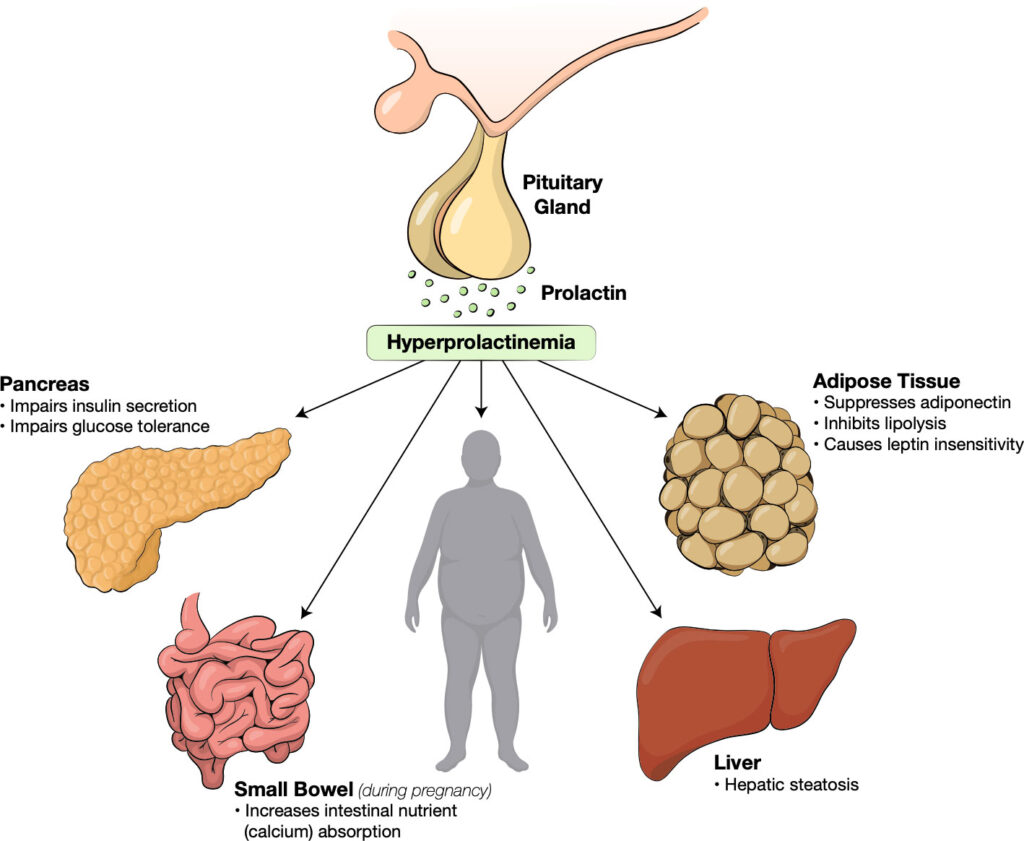
Hyperprolactinemia refers to an abnormal increase in prolactin hormone levels in the blood. Prolactin, produced by the pituitary gland, plays a vital role in lactation and reproductive health. Elevated prolactin can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to various health issues.
Causes of Hyperprolactinemia
Physiological Causes
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Stress
- Physical exertion
Pathological Causes
- Pituitary Tumors (Prolactinomas): Benign tumors in the pituitary gland that secrete excess prolactin.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid can increase TRH levels, stimulating prolactin production.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can reduce prolactin clearance.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal imbalance can elevate prolactin levels.
Medication-Induced Causes
Certain drugs can increase prolactin, including:
- Antipsychotics (e.g., risperidone, haloperidol)
- Antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs, tricyclics)
- Dopamine antagonists (e.g., metoclopramide)
Idiopathic Hyperprolactinemia
In some cases, no identifiable cause is found, classified as idiopathic hyperprolactinemia.
Symptoms of Hyperprolactinemia
In Women
- Irregular menstrual cycles or amenorrhea
- Galactorrhea (milk discharge unrelated to breastfeeding)
- Infertility
- Reduced libido
- Vaginal dryness
In Men
- Erectile dysfunction
- Reduced sperm count
- Gynecomastia (breast enlargement)
- Decreased muscle mass
In Both Genders
- Headaches
- Visual disturbances (linked to pituitary tumors)
- Osteoporosis
- Fatigue and mood changes
Diagnosing Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin Blood Test
A simple blood test measures prolactin levels. Normal values are typically:
- Men: < 20 ng/mL
- Women (non-pregnant): < 25 ng/mL
- Pregnant Women: Up to 200 ng/mL
Additional Diagnostic Tests
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Used to detect pituitary tumors.
- Thyroid Function Tests: Evaluates hypothyroidism as a potential cause.
- Visual Field Tests: Performed if a pituitary tumor is suspected.
Treatment Options for Hyperprolactinemia
Medication
- Dopamine Agonists: Primary treatment to reduce prolactin levels and shrink pituitary tumors. Common drugs include:
- Cabergoline (preferred due to fewer side effects)
- Bromocriptine
Surgical Intervention
- Transsphenoidal Surgery: Required for large pituitary tumors or cases resistant to medication.
Radiation Therapy
- Used when medications and surgery fail to control tumor growth.
Managing Underlying Conditions
- Treating hypothyroidism or adjusting medications may resolve hyperprolactinemia in some cases.
Complications of Untreated Hyperprolactinemia
- Infertility
- Osteoporosis
- Vision impairment (from pituitary tumors)
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Management
- Regular thyroid check-ups
- Monitoring medications that may impact prolactin levels
- Stress management techniques such as meditation and yoga
- Maintaining a balanced diet to support hormonal health
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary cause of hyperprolactinemia?
Pituitary tumors (prolactinomas) are the most common cause of elevated prolactin levels.
How is hyperprolactinemia diagnosed?
A prolactin blood test is the primary diagnostic tool, often followed by MRI for tumor detection.
Can hyperprolactinemia cause infertility?
Yes, elevated prolactin can disrupt reproductive hormones, leading to infertility.
What is the most effective treatment for hyperprolactinemia?
Dopamine agonists like cabergoline are considered the most effective treatment.
Can resolve on its own?
In some cases, particularly mild cases caused by stress or medications, prolactin levels may normalize without intervention.