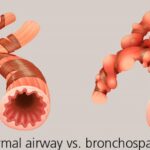
Bronchospasm, a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles, is a critical condition affecting individuals with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory disorders. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies is essential for managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive guide outlines actionable insights into bronchospasm prevention and management.
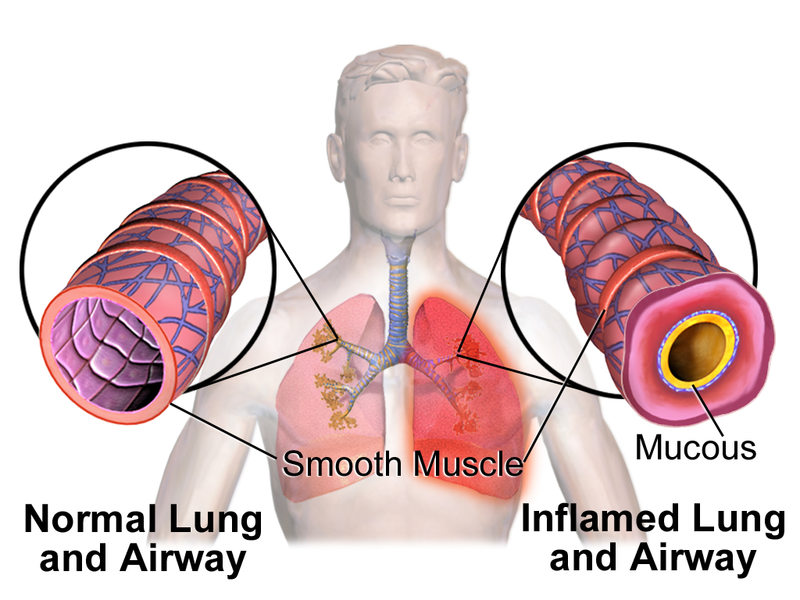
What is Bronchospasm?
Bronchospasm refers to the tightening of the airway muscles, leading to narrowed airways and restricted airflow. This condition often manifests as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, potentially escalating to life-threatening scenarios without timely intervention.
Common Causes and Triggers
Identifying the causes and triggers of bronchospasm is the first step in prevention. Below are some primary factors:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Irritants: Smoke, strong odors, and chemical fumes.
- Exercise: Vigorous physical activity, particularly in cold or dry air.
- Infections: Respiratory infections like colds or bronchitis.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as beta-blockers and aspirin.
- Emotional Stress: High levels of anxiety or stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Symptoms of Bronchospasm
Early detection of symptoms is crucial for prompt treatment. Typical signs include:
- Wheezing
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue during physical activity
Prevention Strategies for Bronchospasm
1. Avoid Known Triggers
Minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants is paramount. Use air purifiers, maintain cleanliness, and avoid smoking.
2. Medication Management
For individuals with asthma or COPD, adhering to prescribed medications like bronchodilators and corticosteroids can prevent episodes.
3. Regular Exercise
While exercise-induced bronchospasm is common, gradual warm-ups, breathing exercises, and controlled environments can reduce risk.
4. Vaccinations
Prevent respiratory infections by staying up-to-date with influenza and pneumococcal vaccines.
5. Stress Reduction Techniques
Incorporate relaxation methods such as meditation and deep breathing to manage emotional stress.
Diagnosing and Treating Bronchospasm
Early diagnosis often involves spirometry tests and clinical evaluations. Treatments typically include:
- Rescue Inhalers: For immediate relief.
- Long-term Medications: To control underlying conditions.
- Allergy Management: Antihistamines and immunotherapy for allergen-induced bronchospasm.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Immediate medical attention is necessary if bronchospasm symptoms worsen despite using rescue medications or if severe breathlessness occurs.
Bronchospasm is a manageable condition with the right preventive strategies and treatment plans. By understanding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying proactive in care, individuals can significantly reduce the risk and impact of this respiratory challenge
MYHEALTHMAG