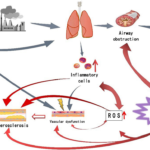
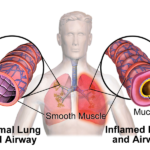
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that significantly impacts the airways, often leading to bronchospasms—sudden contractions of the bronchial muscles that restrict airflow. Effective bronchospasm prevention is crucial for individuals with asthma to ensure better respiratory health and quality of life. In this guide, we delve into the causes, triggers, and strategies to manage and prevent bronchospasms in asthma patients.
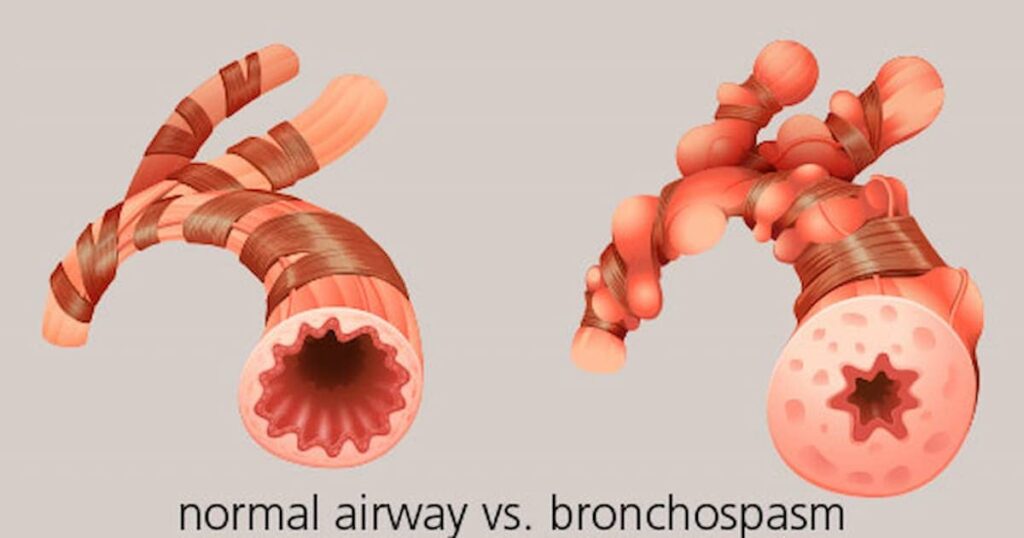
Understanding Bronchospasms in Asthma
What Are Bronchospasms?
Bronchospasms occur when the smooth muscles surrounding the airways tighten, causing narrowing and inflammation. This leads to symptoms such as:
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
How Asthma Triggers Bronchospasms
Asthma heightens the sensitivity of airways, making them prone to spasms when exposed to certain stimuli. These triggers often include allergens, irritants, and respiratory infections.
Identifying Common Triggers
Environmental Factors
- Allergens: Dust mites, pollen, mold, and pet dander are common culprits.
- Irritants: Tobacco smoke, strong odors, and air pollution exacerbate airway sensitivity.
Lifestyle and Activity-Related Triggers
- Exercise: Strenuous activities can induce exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB).
- Weather Changes: Cold air and sudden temperature fluctuations can aggravate symptoms.
Health-Related Triggers
- Infections: Respiratory infections like colds or flu can worsen asthma.
- Medication Sensitivities: Drugs such as aspirin or beta-blockers may provoke reactions in sensitive individuals.
Strategies for Bronchospasm Prevention
1. Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and minimizing exposure to triggers is the first line of defense.
- Use air purifiers and dehumidifiers to maintain clean indoor air.
- Wear masks during high pollen seasons or in polluted environments.
2. Proactive Medication Use
Asthma medications play a vital role in preventing bronchospasms:
- Long-Term Control Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting beta-agonists reduce inflammation and airway sensitivity.
- Quick-Relief Medications: Short-acting beta-agonists provide immediate relief during acute bronchospasms.
3. Developing an Asthma Action Plan
Work with a healthcare provider to create a tailored plan, including:
- Daily medication schedules
- Steps to take during an asthma attack
- Guidelines for emergency care
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Regular Exercise: Moderate physical activity strengthens respiratory muscles but should be performed with proper warm-ups.
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can support respiratory health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga and mindfulness can reduce stress-related exacerbations.
5. Immunotherapy and Vaccinations
- Allergy shots can reduce sensitivity to specific allergens over time.
- Annual flu vaccines and pneumococcal vaccines protect against infections that may worsen asthma symptoms.
Monitoring and Early Intervention
Recognizing Warning Signs
Promptly addressing early symptoms like increased wheezing or coughing can prevent severe bronchospasms. Use peak flow meters to monitor lung function regularly.
Emergency Preparedness
Always carry quick-relief inhalers and ensure close contacts know how to assist during an asthma attack. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist despite medication.Bronchospasm prevention with asthma requires a multifaceted approach encompassing trigger management, medication adherence, and proactive lifestyle changes. By adopting these strategies and maintaining close communication with healthcare providers, individuals with asthma can effectively minimize bronchospasms and enhance their quality of life.