Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic condition characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. Among its many complications, bronchospasm—a sudden narrowing of the airways—can significantly impact quality of life. This guide outlines effective strategies for bronchospasm prevention in COPD, addressing key triggers, treatments, and lifestyle adjustments.
Understanding Bronchospasm in COPD
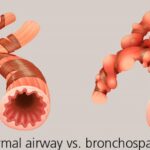
What is Bronchospasm?
Bronchospasm is the involuntary constriction of the smooth muscles in the bronchi, leading to narrowed airways. This results in symptoms such as:
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
The Link Between COPD and Bronchospasm
In COPD, chronic inflammation and structural changes in the lungs predispose individuals to bronchospasm. Understanding the relationship between COPD and bronchospasm is essential for effective prevention and management.
Identifying Triggers of Bronchospasm in COPD
Common Triggers
Recognizing triggers is the first step in prevention. Common bronchospasm triggers for individuals with COPD include:
- Environmental Irritants:
- Tobacco smoke
- Air pollution
- Pollen and allergens
- Respiratory Infections:
- Viral infections like the flu
- Bacterial infections causing pneumonia
- Cold Air and Weather Changes: Sudden exposure to cold air can provoke bronchospasm in sensitive airways.
- Physical Exertion: Overexertion during exercise or daily activities may exacerbate symptoms.
- Medications and Chemicals: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, and exposure to strong odors or chemicals can act as triggers.
Strategies for Bronchospasm Prevention
1. Avoiding Triggers
Minimizing exposure to known triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of bronchospasms.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is critical for preventing airway irritation.
- Use Air Purifiers: Keep indoor air clean and free from pollutants.
- Monitor Weather Conditions: Wear a mask or scarf during cold weather to warm the air before inhalation.
2. Medication Management
Medications play a pivotal role in managing COPD and preventing bronchospasms.
- Bronchodilators: Short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators relax airway muscles, improving airflow.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: Reduce airway inflammation and lower the risk of exacerbations.
- Combination Inhalers: Provide dual benefits of bronchodilation and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Rescue Medications: Use fast-acting inhalers during acute episodes.
3. Respiratory Therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation and breathing exercises improve lung function and resilience.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Strengthens the diaphragm, enhancing respiratory efficiency.
- Pursed-Lip Breathing: Helps maintain open airways and reduces breathlessness.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Regular Vaccinations: Get flu and pneumonia vaccines to prevent respiratory infections.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants supports overall lung health.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated to keep mucus thin and easier to clear.
5. Emergency Preparedness
- Action Plan: Develop a COPD action plan with your healthcare provider.
- Emergency Kit: Include medications, inhalers, and contact information for emergencies.
The Role of Medical Supervision
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure optimal COPD management. Spirometry tests and imaging help monitor disease progression, and timely adjustments to treatment plans prevent complications like bronchospasms.Preventing bronchospasms in COPD requires a proactive approach that includes identifying triggers, adhering to prescribed treatments, and making lifestyle adjustments. By following these strategies, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the burden of COPD.
For personalized advice, consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention and consistent management are key to minimizing complications and maintaining respiratory health.