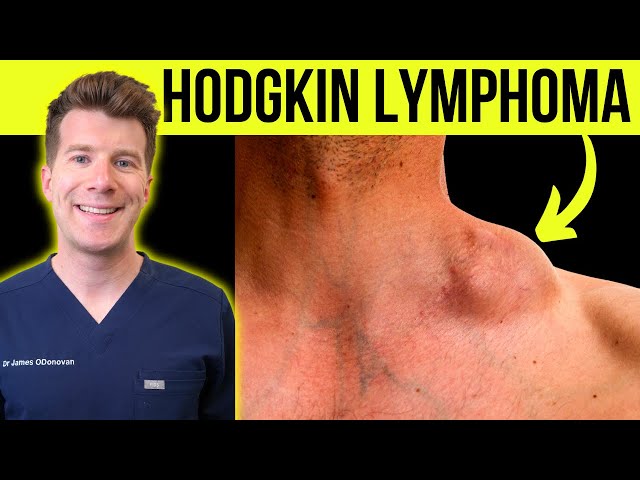
Hodgkin’s lymphoma, also known as Hodgkin’s disease, is a type of lymphoma that affects the lymphatic system, a crucial part of the immune system. This malignancy is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which distinguish it from other forms of lymphoma.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Hodgkin’s lymphoma remains unclear, but several factors increase the risk:
- Age: Commonly affects individuals between 15-30 and over 55.
- Gender: Slightly more prevalent in males.
- Family History: Higher risk if a close relative has lymphoma.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV): Infection increases susceptibility.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS raise the risk.
Common Symptoms of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Symptoms may vary but often include:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes (neck, armpits, or groin)
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained fever
- Night sweats
- Unintentional weight loss
- Itchy skin
- Increased sensitivity to alcohol with lymph node pain
Types of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
There are two primary types:
- Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (cHL): More common, marked by Reed-Sternberg cells.
- Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NLPHL): Rarer form, slower progression.
Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Subtypes
- Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (most common)
- Mixed Cellularity Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Lymphocyte-Rich Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Lymphocyte-Depleted Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Diagnostic Methods
Effective diagnosis often involves:
- Physical Examination
- Blood Tests
- Imaging Tests (CT, PET, or MRI scans)
- Lymph Node Biopsy
- Bone Marrow Biopsy (if needed)
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the stage and type of Hodgkin’s lymphoma:
1. Chemotherapy
- Often the primary treatment for Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Common regimens include ABVD (Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Dacarbazine) and BEACOPP.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Targeted radiation may follow chemotherapy to eliminate residual cancer cells.
3. Immunotherapy
- Drugs like nivolumab and pembrolizumab enhance immune response against cancer cells.
4. Stem Cell Transplant
- Recommended for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
5. Targeted Therapy
- Drugs such as brentuximab vedotin target CD30-positive cells.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is considered one of the most treatable cancers. The 5-year survival rate exceeds 85% for early-stage diagnoses and remains high even in advanced stages with effective treatment.
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
While prevention is challenging, adopting a healthy lifestyle may reduce risks:
- Maintaining a strong immune system
- Avoiding exposure to known risk factors
- Regular medical checkups if at higher risk
FAQs
Q1. Is Hodgkin’s lymphoma curable?
Yes, it is highly curable, especially when detected early.
Q2. What is the main difference between Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells, whereas non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma lacks these cells.
Q3. Can Hodgkin’s lymphoma recur?
Yes, but recurrence can often be managed with additional treatments like chemotherapy or stem cell transplants.
Q4. How is Hodgkin’s lymphoma staged?
Staging is based on the number and location of affected lymph nodes and whether the disease has spread beyond the lymphatic system.
Q5. Are there long-term side effects from treatment?
Possible side effects include fatigue, fertility issues, and increased risk of secondary cancers, but these are often manageable.
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a highly treatable cancer with promising survival rates when diagnosed early. With advancements in therapies like immunotherapy and targeted drugs, patients now have better outcomes and improved quality of life. Early detection, combined with comprehensive treatment strategies, remains key to successful recovery.