A high output ileostomy occurs when an ileostomy produces an excessive amount of stoma output, typically exceeding 1,200 milliliters per day. This condition can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and malnutrition, necessitating careful management to maintain health and quality of life.
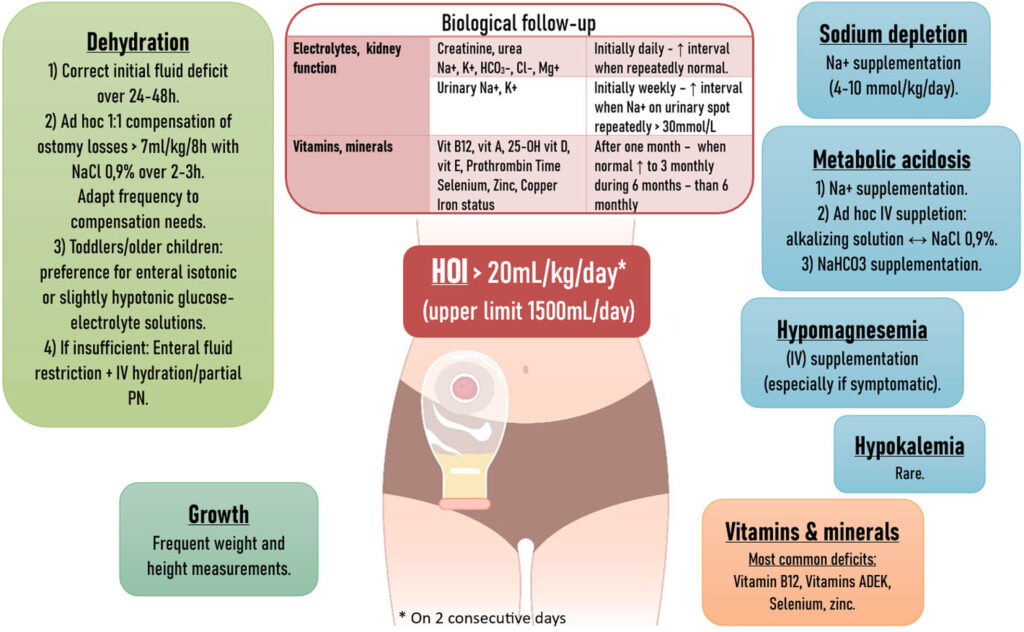
Understanding High Output Ileostomy
An ileostomy is a surgical procedure that brings a portion of the small intestine (ileum) to the abdominal surface, creating a stoma for waste elimination. When the output from this stoma is consistently high, it can hinder the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients and fluids. Factors contributing to a high output stoma include recent surgery, certain medical conditions, and specific medications.
Potential Complications
If not properly managed, a high output ileostomy can result in several complications:
- Dehydration: Excessive fluid loss can lead to symptoms such as dry mouth, increased thirst, dizziness, and decreased urine output.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Loss of vital salts like sodium and potassium may cause muscle cramps, weakness, and cardiac issues.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate absorption of nutrients can result in weight loss, fatigue, and a weakened immune system.
Management Strategies
Effective management of a high output ileostomy involves a combination of dietary adjustments, medication, and fluid management:
- Dietary Modifications:
- Increase Salt Intake: Incorporate salt into meals and consume salty foods to compensate for sodium loss.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Opt for low-fiber foods to reduce bowel movements. Choose white bread, rice, and pasta over whole-grain alternatives, and peel fruits and vegetables before consumption.
- Fluid Management:
- Oral Rehydration Solutions: Instead of plain water, drink rehydration solutions containing the right balance of salts and sugars to promote fluid absorption.
- Limit Hypotonic Fluids: Reduce intake of beverages like plain water, tea, and coffee, as they can increase stoma output.
- Medications:
- Anti-diarrheal Agents: Medications such as loperamide can slow bowel movements, reducing output.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs like omeprazole decrease gastric secretions, aiding in fluid retention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent high stoma output despite management efforts.
- Signs of dehydration, such as dizziness or decreased urine output.
- Blood in the stoma output or severe abdominal pain.
Managing a high output ileostomy requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, proper hydration, and appropriate medication. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals ensures effective management and minimizes potential complications, thereby enhancing overall well-being.