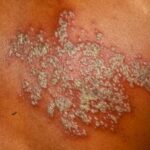
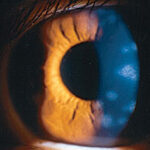
Herpes zoster hepatitis is a rare yet serious condition that occurs when the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) causes inflammation of the liver. While VZV is commonly known for causing chickenpox and shingles, in some cases, it can lead to hepatitis, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
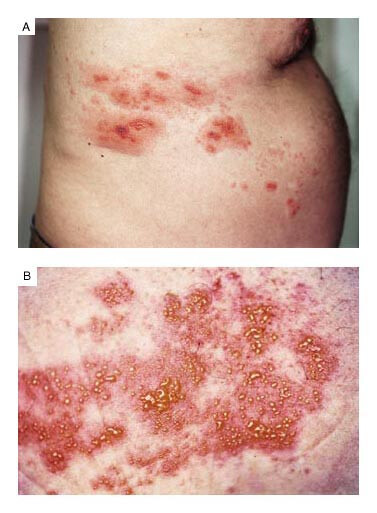
Causes of Herpes Zoster Hepatitis
Herpes zoster hepatitis is triggered by the reactivation of the dormant varicella-zoster virus, usually in people with weakened immune systems. Common risk factors include:
- HIV/AIDS
- Organ transplantation
- Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy
- Long-term corticosteroid use
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster Hepatitis
The symptoms of herpes zoster hepatitis can vary in severity. Common signs include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and malaise
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
- Fever and chills
Diagnosis of Herpes Zoster Hepatitis
A proper diagnosis involves:
- Blood Tests: Elevated liver enzymes (AST, ALT) and abnormal bilirubin levels.
- PCR Test: Identifies VZV DNA in blood or tissue samples.
- Liver Biopsy: Confirms VZV-induced inflammation in severe cases.
Potential Complications
If untreated, herpes zoster hepatitis can lead to:
- Acute liver failure
- Multi-organ dysfunction
- Severe systemic infections
- Prolonged hospital stay
Treatment for Herpes Zoster Hepatitis
Effective treatment strategies include:
- Antiviral Therapy: Acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir to control VZV replication.
- Corticosteroids: Used in some cases to reduce inflammation.
- Supportive Care: Includes hydration, electrolyte management, and nutritional support.
Preventing Herpes Zoster Hepatitis
Prevention is critical, particularly for at-risk groups. Key measures include:
- Vaccination: The shingles vaccine can reduce the risk of VZV reactivation.
- Immune System Support: Adequate nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
- Early Detection: Prompt medical attention for shingles symptoms can prevent complications.
Prognosis and Recovery
With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most patients recover well. However, in individuals with weakened immunity, the condition can become life-threatening, emphasizing the importance of proactive healthcare.
Herpes zoster hepatitis is a rare but critical condition requiring prompt medical intervention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is vital for managing and preventing severe complications. Individuals with compromised immunity should prioritize vaccination and seek immediate care if they experience concerning symptoms.