What is Bulimia Nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa is a serious eating disorder characterized by a recurring cycle of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as self-induced vomiting, excessive exercise, or the misuse of laxatives. This condition often stems from an intense fear of weight gain and a distorted self-image. Despite fluctuations in weight, individuals with bulimia nervosa often maintain a body weight within the normal range, making it harder to detect externally.
Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
Recognizing the symptoms of bulimia nervosa is essential for early intervention. Common signs include:
- Behavioral Symptoms:
- Frequent episodes of consuming large quantities of food in a short period (binge eating).
- Compensatory behaviors, such as vomiting, fasting, or excessive exercise.
- Secretive eating or hiding food.
- Physical Symptoms:
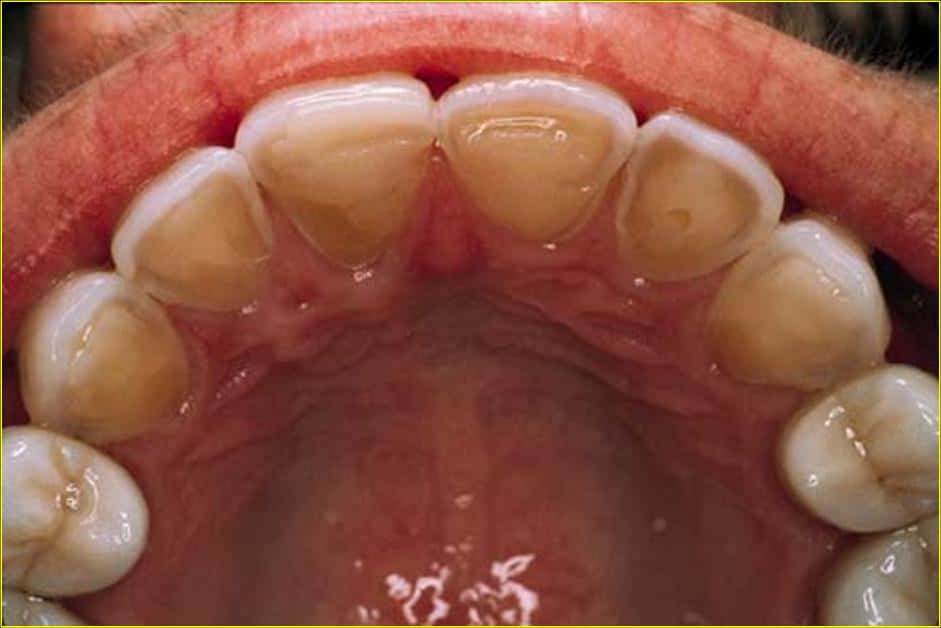
- Swollen salivary glands and dental erosion due to repeated vomiting.
- Chronic sore throat and gastrointestinal issues.
- Fluctuating weight and dehydration.
- Emotional Symptoms:
- Extreme fear of gaining weight.
- Feelings of shame, guilt, or lack of control after binge eating.
- Anxiety and depression.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of bulimia nervosa is multifactorial, involving biological, psychological, and sociocultural influences.
Biological Factors
- Genetics: Family history of eating disorders or mental health conditions.
- Neurochemical Imbalances: Dysregulation of serotonin and dopamine may contribute to binge-purge behaviors.
Psychological Factors
- Low Self-Esteem: Individuals with bulimia often struggle with body dissatisfaction.
- Trauma or Abuse: Adverse childhood experiences can increase vulnerability.
Sociocultural Factors
- Cultural Pressure: Societal emphasis on thinness and unrealistic beauty standards.
- Media Influence: Exposure to images promoting unattainable body ideals.
Diagnosis of Bulimia Nervosa
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough assessment by healthcare professionals, including:
- Clinical Interviews: Discussions about eating habits, behaviors, and psychological health.
- Physical Examination: Checking for physical signs associated with bulimia.
- DSM-5 Criteria: Meeting diagnostic criteria as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Health Complications
Bulimia nervosa can lead to severe health issues if left untreated:
- Cardiovascular Problems: Electrolyte imbalances can cause arrhythmias.
- Gastrointestinal Damage: Chronic vomiting may result in esophageal tears or acid reflux.
- Dental Decay: Exposure to stomach acid damages tooth enamel.
- Mental Health Disorders: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
Treatment Options for Bulimia Nervosa
Effective treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual’s needs.
Psychological Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on altering unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): Addresses relationship issues that may contribute to bulimia.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Helps manage emotional regulation and impulsivity.
Medical Interventions
- Nutritional Counseling: Education on balanced eating and meal planning.
- Medications: Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are sometimes prescribed.
Support Groups
Peer-led or professionally guided groups provide emotional support and shared experiences, fostering a sense of community in recovery.
Recovery and Coping Strategies
Recovery from bulimia nervosa is possible with persistence and professional guidance. Strategies include:
- Building a Support Network: Family, friends, and therapists play a vital role.
- Mindfulness Practices: Techniques such as meditation can help manage stress and emotional triggers.
- Journaling: Tracking eating habits and emotions to identify patterns and triggers.
Prevention
Preventative measures focus on promoting healthy relationships with food and body image:
- Educating Youth: Teaching resilience against societal pressures.
- Encouraging Open Communication: Creating safe spaces to discuss mental health.
- Advocating Media Literacy: Critical evaluation of unrealistic portrayals in media.
Its a complex but treatable condition. Early recognition, comprehensive treatment, and a strong support system are pivotal in overcoming this disorder. If you or someone you know may be struggling with bulimia nervosa, seeking professional help is the first step towards recovery.