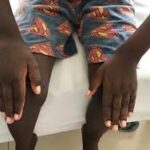
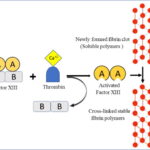
Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by impaired blood clotting due to insufficient or malfunctioning Factor X protein. This condition is classified as a bleeding disorder and is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
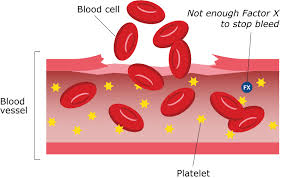
What is Factor X?
Factor X, also known as Stuart-Prower factor, is a critical coagulation protein produced in the liver. It plays a vital role in the coagulation cascade, converting prothrombin into thrombin to facilitate clot formation.
Causes of Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease
Hereditary Factor X Deficiency is caused by mutations in the F10 gene, responsible for coding the Factor X protein. Individuals inherit this disorder in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene.
Genetic Mutation Types
- Missense mutations: Result in amino acid changes impacting protein function.
- Nonsense mutations: Cause premature stop codons, leading to incomplete protein synthesis.
- Frameshift mutations: Shift the gene’s reading frame, producing nonfunctional proteins.
Symptoms of Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of Factor X deficiency. Common signs include:
- Excessive bruising
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Prolonged bleeding after injuries or surgeries
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Joint and muscle bleeding in severe cases
Diagnosis of Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease
Diagnosing Factor X deficiency involves:
- Prothrombin Time (PT): Prolonged PT indicates clotting issues.
- Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT): Prolonged aPTT suggests intrinsic pathway defects.
- Factor X Activity Test: Confirms the level of functional Factor X protein.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies specific mutations in the F10 gene.
Treatment Options for Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease
Management strategies include:
- Plasma-derived Factor X concentrates: Effective for acute bleeding episodes and surgical procedures.
- Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP): Contains multiple clotting factors, including Factor X.
- Prothrombin Complex Concentrates (PCCs): Provide Factor X along with other essential coagulation proteins.
- Vitamin K Supplementation: Beneficial in cases of mild deficiency.
Long-Term Management
- Regular monitoring of clotting factor levels.
- Prophylactic treatment in severe cases to prevent spontaneous bleeding.
- Genetic counseling for affected families to assess inheritance risks.
Complications Associated with Factor X Deficiency
Without appropriate treatment, Factor X deficiency can lead to:
- Severe internal bleeding
- Hemarthrosis (bleeding into joints)
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
Prognosis for Patients with Factor X Deficiency
With proper treatment and regular follow-up, patients can maintain a relatively normal lifestyle. Early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention significantly improve outcomes.
Prevention Strategies
- Carrier Screening: Identifies at-risk individuals, especially in families with a known history.
- Prenatal Testing: Allows early diagnosis for informed medical decisions.
FAQs:
What are the early signs of Factor X deficiency?
Early signs often include unexplained bruising, prolonged nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual periods.
Is Factor X deficiency life-threatening?
Severe cases may result in life-threatening bleeding complications, particularly if untreated.
Can Factor X deficiency be cured?
While there is no permanent cure, effective management strategies provide long-term control.
How rare is hereditary Factor X deficiency?
The condition occurs in approximately 1 in 500,000 to 1 in 1,000,000 individuals worldwide.
Are there lifestyle changes for managing this condition?
Patients should avoid activities with a high risk of injury, and adopt a healthy diet supporting liver function.
Hereditary Factor X Deficiency Disease is a rare but manageable condition. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive care are essential for improving patient outcomes. Awareness of this disorder and proactive medical management significantly enhance quality of life.