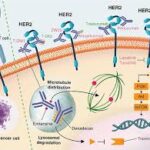
HER2-positive adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) is a rare yet aggressive malignancy that requires targeted treatment strategies. This condition is characterized by the overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein, which promotes tumor cell proliferation.
Understanding HER2 in Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer
HER2 is a transmembrane receptor involved in cell growth and differentiation. Its overexpression in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma is associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and a poorer prognosis.
Risk Factors for HER2-Positive GEJ Adenocarcinoma
- Chronic Gastric Reflux: Persistent acid exposure leads to Barrett’s esophagus, increasing cancer risk.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These habits are linked to higher GEJ cancer incidence.
- Obesity: Excessive abdominal fat raises intra-abdominal pressure, worsening reflux.
- Dietary Factors: High intake of processed foods and low fruit/vegetable consumption can increase risk.
- Genetics: Family history of gastroesophageal cancers may contribute.
Diagnostic Procedures for HER2-Positive GEJ Adenocarcinoma
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Endoscopy with Biopsy: Provides direct visualization and tissue sampling.
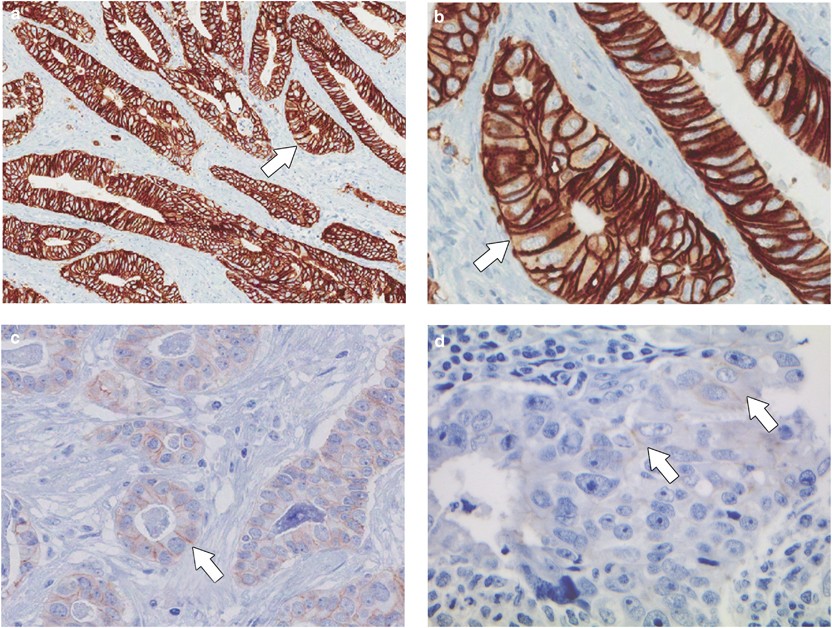
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Determines HER2 protein overexpression on cancer cells.
- Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH): Confirms HER2 gene amplification in ambiguous IHC results.
- CT and PET Scans: Aid in staging by identifying metastatic spread.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Evaluates tumor depth and lymph node involvement.
Staging and Classification
The TNM staging system is the standard approach for evaluating GEJ adenocarcinoma.
Treatment Options for HER2-Positive GEJ Adenocarcinoma
Management strategies depend on the cancer stage, patient health, and HER2 status.
1. Targeted Therapy
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin): A monoclonal antibody that targets HER2 receptors, improving survival rates in combination with chemotherapy.
- Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (Enhertu): An advanced antibody-drug conjugate approved for HER2-positive GEJ cancer with metastatic progression.
2. Chemotherapy
Common regimens include:
- FOLFOX (5-FU, Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin)
- CAPOX (Capecitabine and Oxaliplatin)
3. Surgery
For localized tumors, esophagectomy or total gastrectomy may be recommended. Surgical resection aims to achieve clear margins and improve survival outcomes.
4. Radiation Therapy
Used alongside chemotherapy or post-surgery to target residual tumor cells and minimize recurrence risk.
5. Immunotherapy
Checkpoint inhibitors like nivolumab and pembrolizumab may be used in HER2-positive cases with high PD-L1 expression.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis for HER2-positive GEJ adenocarcinoma is influenced by:
- Cancer Stage: Early-stage cancers have better outcomes.
- Treatment Response: Patients responding well to HER2-targeted therapies show improved survival.
- Overall Health: Comorbidities can affect treatment success.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol: These substances can worsen prognosis.
- Regular Exercise: Improves immunity and treatment tolerance.
- Follow-Up Care: Routine checkups ensure early detection of recurrence.
FAQs
Q1. What is HER2-positive GEJ adenocarcinoma?
A type of cancer located at the gastroesophageal junction marked by excess HER2 protein expression.
Q2. How is HER2-positive GEJ cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis is confirmed using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
Q3. Is HER2-positive GEJ cancer curable?
While aggressive, effective treatment combining targeted therapy and surgery can improve outcomes significantly.
Q4. What is the survival rate for HER2-positive GEJ adenocarcinoma?
Survival rates vary; early detection and HER2-targeted therapies improve prognosis.
Q5. What role does trastuzumab play in treatment?
Trastuzumab effectively targets HER2 receptors, enhancing chemotherapy outcomes and improving survival.
HER2-positive adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction presents unique treatment challenges. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary treatment approach involving targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle changes and adhere to post-treatment care for optimal recovery.