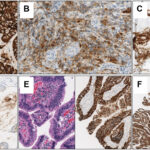
Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a rare but significant subtype of lung cancer characterized by specific genetic alterations. These mutations drive cancer growth and present unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the molecular landscape of HER2 mutations is crucial for effective clinical management.
Understanding HER2 Mutations in NSCLC
HER2 mutations are distinct from HER2 amplifications or overexpression. In NSCLC, HER2 mutations typically involve exon 20 insertions, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation.
Key Characteristics of HER2 Mutations
- Exon 20 Insertions: Found in approximately 1-4% of NSCLC cases.
- Oncogenic Driver: Promotes aggressive tumor growth.
- Targetable Mutation: Emerging therapies are designed specifically to inhibit HER2-driven pathways.
Risk Factors and Epidemiology
- Smoking: Limited correlation compared to other NSCLC types.
- Gender Predisposition: More prevalent in women.
- Ethnic Variations: Higher incidence in East Asian populations.
- Non-Smokers: Often occurs in individuals with no history of smoking.
Symptoms of HER2 Mutant NSCLC
Patients may exhibit symptoms similar to other NSCLC subtypes, including:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Diagnostic Techniques for HER2 Mutant NSCLC
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to distinguish HER2 mutations from other molecular alterations in NSCLC.
Common Diagnostic Methods
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): The most precise method for identifying HER2 exon 20 insertions.
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Used to detect HER2 overexpression but less effective for mutations.
- Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH): Identifies HER2 gene amplifications, occasionally used in combination with NGS.
Treatment Options for HER2 Mutant NSCLC
Treatment approaches for HER2-mutant NSCLC are evolving, with targeted therapies showing improved outcomes.
Targeted Therapies
- Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (T-DXd): A promising antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) with high efficacy in HER2-mutant NSCLC.
- Mobocertinib: An oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) effective against exon 20 insertions.
- Poziotinib: Another TKI designed to target HER2 mutations, though toxicity concerns require careful monitoring.
Immunotherapy
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs): While commonly used in NSCLC, their effectiveness in HER2-mutant cases may be limited without combination strategies.
Chemotherapy
- Traditional platinum-based chemotherapy remains a viable option for patients ineligible for targeted treatments.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research is exploring novel drug combinations and improved inhibitors. Notable advancements include:
- Bispecific Antibodies: Combining HER2 targeting with other pathways.
- Combination Therapies: Merging ICIs with TKIs for enhanced efficacy.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
HER2-mutant NSCLC generally presents with a poorer prognosis than other driver mutations. Early diagnosis and access to targeted treatments significantly improve survival outcomes.
Key Prognostic Factors
- Disease stage at diagnosis
- Access to targeted therapies
- Overall patient health and response to treatment
Lifestyle and Supportive Care
- Nutritional Support: Emphasizing a balanced diet to manage treatment side effects.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Enhances lung function and quality of life.
- Psychological Support: Ensures emotional well-being during treatment.
FAQs
What is the primary cause of HER2 mutations in NSCLC?
HER2 mutations are primarily genetic alterations rather than being directly linked to lifestyle factors such as smoking.
Are HER2 mutations common in lung cancer?
HER2 mutations are relatively rare, accounting for 1-4% of NSCLC cases.
How is HER2-mutant NSCLC treated?
Targeted therapies such as trastuzumab deruxtecan and mobocertinib are key treatment options.
Can immunotherapy be effective for HER2-mutant NSCLC?
Immunotherapy alone may have limited impact; however, combination strategies are showing promise.
Is there a cure for HER2-mutant NSCLC?
While not yet curable, ongoing advancements in targeted treatments are improving long-term outcomes.
HER2 mutant non-small cell lung cancer requires precise diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. With advancements in targeted therapies and ongoing clinical research, patients diagnosed with this rare subtype have increasingly promising options for effective management and improved survival rates.