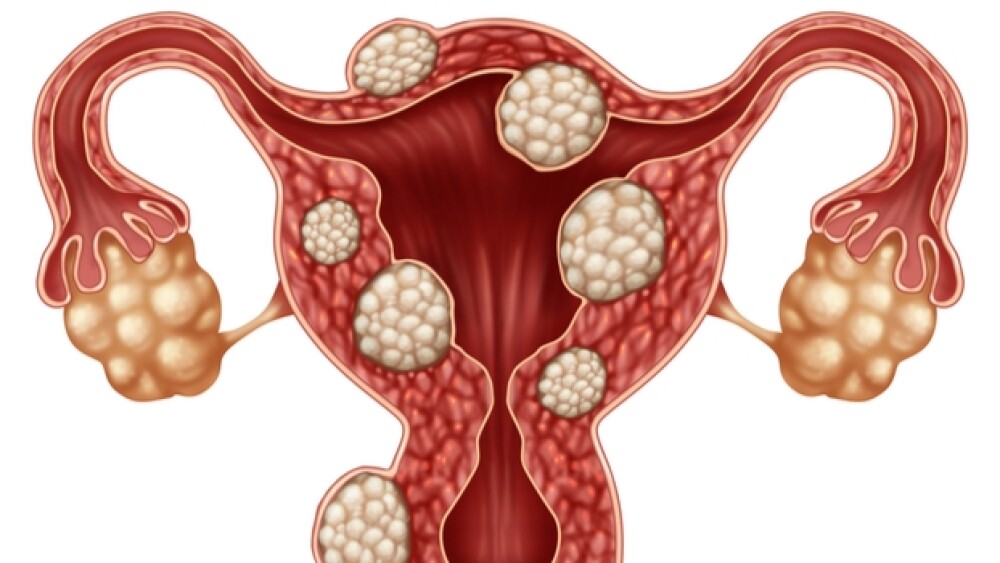
Uterine leiomyoma, also known as fibroids, are non-cancerous tumors that develop in the uterus. These growths can vary in size, number, and location, significantly impacting a woman’s menstrual cycle. One of the most common and debilitating symptoms is heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB).
Causes of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in Uterine Leiomyoma
Heavy menstrual bleeding is a frequent manifestation of uterine fibroids. The primary causes include:
- Increased Vascularization: Fibroids promote excessive blood vessel growth, increasing blood flow during menstruation.
- Uterine Enlargement: Larger fibroids can distort the uterine lining, resulting in prolonged or heavy bleeding.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Elevated estrogen and progesterone levels often stimulate fibroid growth, further impacting menstrual cycles.
- Endometrial Dysfunction: Fibroids can alter the uterine lining’s structure, causing irregular shedding.
Symptoms of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Women with uterine fibroids may experience:
- Prolonged menstrual periods lasting over seven days
- Excessive blood loss requiring frequent sanitary product changes
- Blood clots larger than a quarter
- Symptoms of anemia such as fatigue, weakness, and dizziness
Diagnosis of Uterine Leiomyoma
Diagnosing uterine fibroids involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging techniques:
- Pelvic Examination: Identifies uterine enlargement or irregularities.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Offers a detailed view of fibroid size and location.
- MRI Scan: Provides comprehensive imaging for larger or multiple fibroids.
- Hysteroscopy: A direct visual assessment of the uterine cavity.
Treatment Options for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Treatment strategies vary based on symptom severity, fibroid size, and patient preferences. Options include:
1. Medications
- Hormonal Therapies: Birth control pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can regulate bleeding.
- Non-Hormonal Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or tranexamic acid may reduce blood loss.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): Blocks blood supply to fibroids, reducing their size.
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
3. Surgical Interventions
- Hysterectomy: A definitive solution involving uterine removal, recommended for severe cases.
- Endometrial Ablation: A procedure that destroys the uterine lining to reduce bleeding.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle changes can help manage heavy menstrual bleeding:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to regulate hormonal balance
- Including iron-rich foods to combat anemia
- Practicing relaxation techniques to reduce stress and hormone fluctuations
Complications of Untreated Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
If left unmanaged, heavy menstrual bleeding linked to fibroids may result in:
- Severe anemia requiring blood transfusion
- Chronic fatigue and reduced quality of life
- Fertility challenges due to uterine scarring or distortion
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pelvic pain
- Menstrual cycles longer than seven days
- Dizziness or extreme fatigue from blood loss
Heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine leiomyoma can severely affect daily life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures timely intervention and minimizes complications.