Headache disorders are among the most common nervous system conditions, characterized by recurrent headaches that may vary in intensity, duration, and origin. They significantly affect quality of life and productivity.
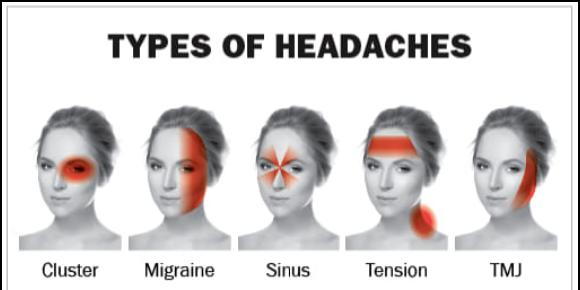
Types of Headache Disorders
Headache disorders are broadly categorized into primary and secondary headaches.
Primary Headaches
Primary headaches are not symptoms of another condition but are standalone disorders. Common types include:
- Migraine: Throbbing pain often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Tension Headache: Dull, aching pain with a sensation of pressure around the head.
- Cluster Headache: Intense, piercing pain that occurs in clusters over weeks or months.
Secondary Headaches
Secondary headaches are caused by underlying medical conditions such as infections, head injuries, or sinus issues. Common types include:
- Sinus Headache: Associated with sinus infections and inflammation.
- Medication Overuse Headache (MOH): Caused by frequent use of pain medications.
Common Causes of Headache Disorders
Several factors contribute to headache disorders, including:
- Genetics: Migraines often run in families.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress is a major trigger for tension headaches.
- Environmental Factors: Noise, bright lights, and strong odors may induce migraines.
- Diet and Lifestyle: Irregular eating patterns, dehydration, and excessive alcohol consumption can trigger headaches.
- Medical Conditions: Hypertension, infections, or neurological issues may lead to secondary headaches.
Symptoms of Headache Disorders
Symptoms vary by type but commonly include:
- Throbbing or pulsating pain
- Pressure or tightness around the forehead
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light, sound, or smells
- Visual disturbances (aura) in migraines
Diagnosis of Headache Disorders
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Assessing the frequency, duration, and triggers of headaches.
- Physical Examination: Checking neurological signs to rule out serious conditions.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans may be conducted for persistent or severe headaches.
Treatment Options for Headache Disorders
Treatment approaches vary depending on the type and severity of the headache disorder.
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Paracetamol, ibuprofen, and aspirin for mild headaches.
- Triptans and Ergotamines: Specifically designed for migraines.
- Preventive Medications: Beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants may reduce migraine frequency.
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a balanced diet are effective preventive measures.
- Identifying and avoiding known triggers can significantly reduce headache occurrences.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Effective for reducing migraine frequency.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps manage stress-induced headaches.
- Herbal Remedies: Feverfew and butterbur may offer relief for some migraine sufferers.
Preventive Strategies
To minimize headache occurrences:
- Maintain consistent sleep patterns.
- Stay hydrated and avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol.
- Manage stress through mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical help if you experience:
- Sudden, severe headaches
- Persistent headaches that worsen over time
- Neurological symptoms such as vision loss, weakness, or confusion
Headache disorders are widespread but manageable with appropriate lifestyle changes, medication, and preventive strategies. Identifying triggers and seeking timely medical advice can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by chronic headaches.