Growth failure secondary to chronic renal failure (CRF) is a significant concern in pediatric nephrology. Children with CRF face challenges in achieving optimal height and development due to multifactorial causes. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and management strategies is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Causes of Growth Failure in Chronic Renal Failure
Several factors contribute to impaired growth in children with CRF:
1. Endocrine Dysregulation
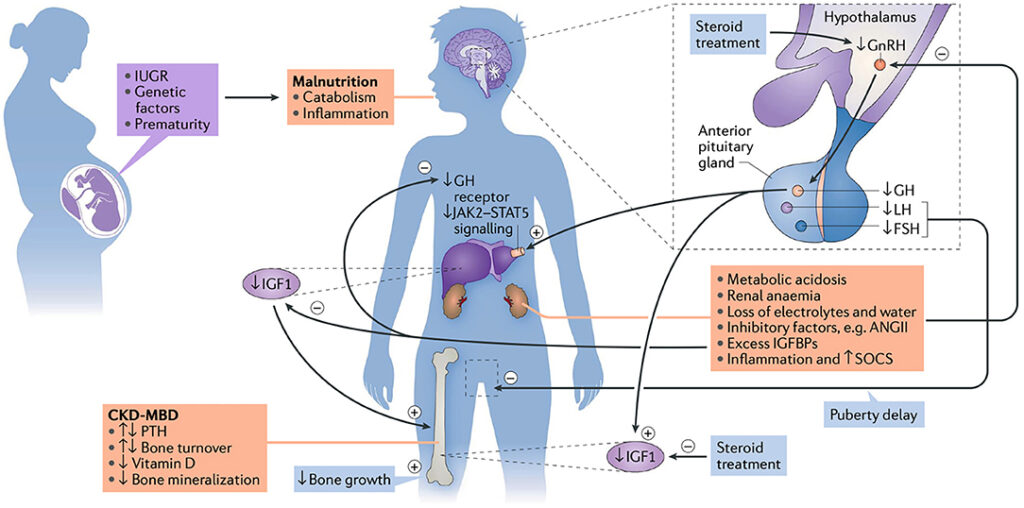
- Impaired production of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) leads to stunted growth.
- Resistance to GH is common in CRF patients despite normal or elevated GH levels.
2. Nutritional Deficiencies
- Poor appetite, dietary restrictions, and gastrointestinal issues reduce caloric and nutrient intake.
- Protein-energy malnutrition is frequently observed in these patients.
3. Metabolic Acidosis
- Chronic metabolic acidosis can impair bone growth and protein synthesis, exacerbating growth failure.
4. Renal Osteodystrophy
- Abnormal bone metabolism due to imbalances in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D affects skeletal growth.
5. Anemia
- Reduced erythropoietin production leads to anemia, resulting in fatigue and reduced physical activity, further impacting growth.
6. Systemic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
- Persistent inflammation in CRF patients contributes to impaired growth through cytokine-mediated processes.
Diagnosis of Growth Failure in CRF
Early identification is key to effective intervention. Diagnostic approaches include:
- Anthropometric Measurements: Regular monitoring of height, weight, and body mass index (BMI).
- Growth Hormone Testing: Assessing GH and IGF-1 levels.
- Nutritional Assessment: Evaluating protein, calorie intake, and vitamin/mineral deficiencies.
- Bone Density Scans: To assess bone health and detect early signs of renal osteodystrophy.
Management Strategies for Growth Failure in CRF
1. Nutritional Support
- High-calorie, protein-rich diets tailored to the patient’s nutritional needs.
- Supplements to address vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate imbalances.
2. Growth Hormone Therapy
- Recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) therapy effectively improves height outcomes in children with CRF.
- Early initiation and consistent monitoring are essential for optimal results.
3. Management of Metabolic Acidosis
- Oral bicarbonate supplements can correct acidosis and improve growth rates.
4. Treatment of Renal Osteodystrophy
- Phosphate binders, vitamin D analogs, and calcium supplements help manage bone health.
5. Anemia Management
- Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and iron supplements improve hemoglobin levels and overall energy.
6. Renal Replacement Therapy
- In severe CRF cases, dialysis or kidney transplantation can restore metabolic balance and improve growth potential.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
With appropriate management, many children with CRF can achieve improved growth outcomes. Early diagnosis, individualized treatment plans, and consistent follow-up play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal results.
Growth failure secondary to chronic renal failure requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach involving nephrologists, endocrinologists, and dietitians. By addressing nutritional, hormonal, and metabolic factors, healthcare providers can significantly improve growth outcomes and overall quality of life for affected children.