Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae, primarily affecting the lungs. While several strains exist, type b (Hib) is the most pathogenic and has been historically responsible for severe infections. This article provides an in-depth examination of the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prevention strategies for Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia.
Causes of Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia
Haemophilus influenzae is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacterium. It can be categorized into two main groups:
- Encapsulated Strains (Typeable): Particularly type b (Hib), known for causing invasive diseases like meningitis and pneumonia.
- Non-Encapsulated Strains (Nontypeable): Often associated with localized respiratory tract infections.
Transmission occurs through respiratory droplets expelled during coughing, sneezing, or close contact. Individuals at increased risk include:
- Infants and young children (especially those unvaccinated)
- Elderly adults
- Immunocompromised patients
- Individuals with chronic lung conditions (e.g., COPD)
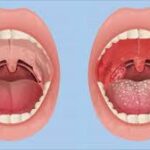
Symptoms of Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia
The clinical presentation of Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia can vary but typically includes:
- Persistent cough (productive or dry)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest pain (pleuritic in nature)
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Purulent sputum production
- Cyanosis (in severe cases)
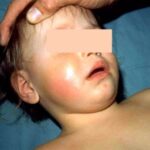
Complications may arise, such as empyema, pleural effusion, or respiratory failure, especially if left untreated.
Diagnosis of Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Key diagnostic procedures include:
- Clinical Evaluation: Thorough patient history and physical examination focusing on respiratory symptoms.
- Microbiological Testing:
- Sputum Culture: Isolation of H. influenzae from sputum samples.
- Blood Culture: For detecting bacteremia in severe cases.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): For rapid and precise bacterial identification.
- Imaging Studies:
- Chest X-ray: Identifies lung consolidation and infiltrates.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed imaging in complicated or ambiguous cases.
Treatment of Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia
Treatment involves prompt antibiotic therapy tailored to bacterial susceptibility. The choice of antibiotics depends on the patient’s clinical status and resistance patterns.
Empiric Antibiotic Therapy:
- Mild to Moderate Cases:
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate
- Cefuroxime
- Doxycycline (for penicillin-allergic patients)
- Severe Cases or Hospitalized Patients:
- Ceftriaxone or Cefotaxime (intravenous)
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., levofloxacin) for beta-lactam intolerance
Duration of Therapy:
- Uncomplicated cases: 7-10 days
- Complicated or immunocompromised cases: 14-21 days
Supportive care may include:
- Oxygen supplementation
- Antipyretics and analgesics
- Intravenous fluids for hydration
Prevention of Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia
Prevention strategies are centered on immunization and public health measures.
Vaccination:
- Hib Vaccine: Recommended for all infants as part of routine immunization.
- Adult Vaccination: For high-risk groups, including those with asplenia or immunodeficiency.
Infection Control:
- Hand hygiene and respiratory etiquette.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis for close contacts in case of invasive disease outbreaks.
Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia remains a significant cause of respiratory morbidity. Early diagnosis and appropriate antimicrobial therapy are essential for patient recovery. Preventive measures, especially widespread vaccination, play a crucial role in reducing the disease burden. With continued public health initiatives, the incidence of severe H. influenzae infections can be further curtailed.