Gonococcal pharyngitis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, primarily affecting the throat. While this condition is less common than genital gonorrhea, it poses significant public health concerns due to its potential to spread undetected.
Causes of Gonococcal Pharyngitis
The primary cause of gonococcal pharyngitis is oral exposure to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This typically occurs through:
- Oral-genital contact
- Oral-anal contact (less common)
- Sharing objects contaminated with infected secretions
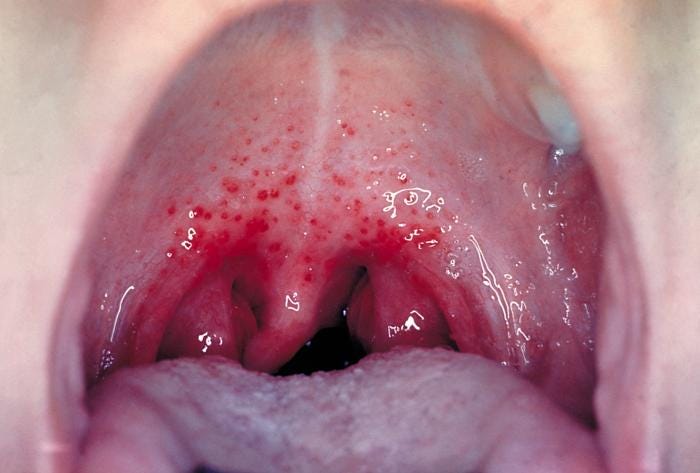
Symptoms of Gonococcal Pharyngitis
Many individuals with gonococcal pharyngitis remain asymptomatic, making early detection challenging. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Redness or irritation in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fever (in severe cases)
- White or yellowish throat exudate
Risk Factors for Gonococcal Pharyngitis
Certain behaviors and conditions increase the risk of gonococcal pharyngitis:
- Engaging in unprotected oral sex
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexual contact with individuals infected with N. gonorrhoeae
- History of other sexually transmitted infections
Diagnosis of Gonococcal Pharyngitis
Diagnosing gonococcal pharyngitis requires specific tests to confirm the presence of N. gonorrhoeae in the throat. Key diagnostic methods include:
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test): The most sensitive and accurate test.
- Throat Swab Culture: Identifies bacterial presence and antibiotic susceptibility.
- Gram Stain Analysis: Less common but useful in confirming bacterial identification.
Complications of Untreated Gonococcal Pharyngitis
If left untreated, gonococcal pharyngitis may lead to:
- Persistent sore throat
- Systemic gonococcal infection
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
- Potential spread to other partners
Treatment of Gonococcal Pharyngitis
The primary treatment for gonococcal pharyngitis involves antibiotics. Recommended treatments include:
- Ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly (IM) as a single dose
- Azithromycin 1g orally (optional, to manage potential co-infections)
Prevention Strategies
Preventing gonococcal pharyngitis involves proactive measures:
- Use of condoms and dental dams during oral sex
- Routine STI screenings for sexually active individuals
- Limiting the number of sexual partners
- Open communication with partners about sexual health
Prognosis and Recovery
With prompt treatment, gonococcal pharyngitis generally resolves within a few days. It is essential to complete the full antibiotic course and undergo follow-up testing to confirm bacterial eradication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can gonococcal pharyngitis be transmitted through kissing?
A: No, transmission through casual kissing is extremely rare; it primarily spreads via oral-genital contact.
Q2: How long does it take for symptoms to appear?
A: Symptoms typically develop within 2-5 days after exposure, but some individuals may remain asymptomatic.
Q3: Is gonococcal pharyngitis contagious?
A: Yes, untreated individuals can transmit the infection through oral sexual contact.
Q4: Can I get gonococcal pharyngitis again after treatment?
A: Yes, reinfection can occur if exposure happens again, underscoring the importance of preventive measures.
Q5: Are home remedies effective for gonococcal pharyngitis?
A: No, antibiotics are the only effective treatment; home remedies may provide symptom relief but cannot cure the infection.
Gonococcal pharyngitis is a manageable condition with timely diagnosis and treatment. Awareness, preventive strategies, and regular STI screening are crucial in reducing transmission rates and protecting public health.