Gonadotropin-releasing factor deficiency (GnRH deficiency) is a rare endocrine disorder characterized by impaired production or action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This condition can lead to delayed or absent puberty, infertility, and other hormonal imbalances.
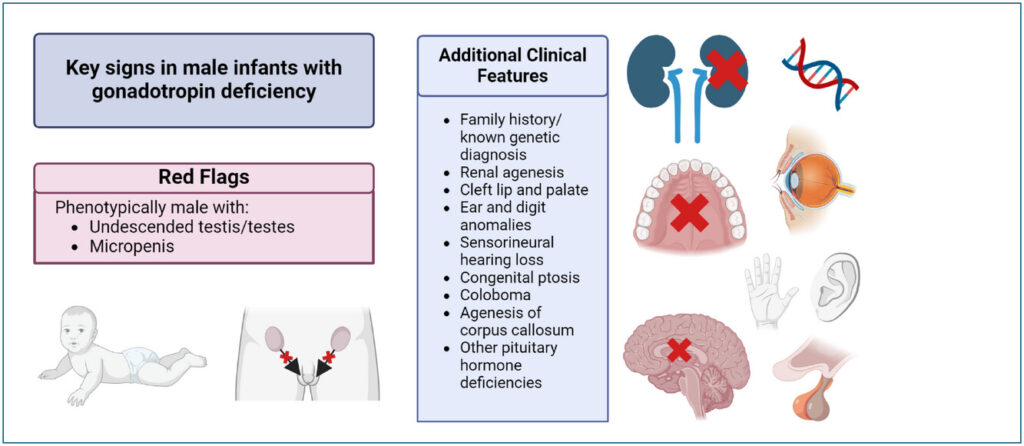
Causes of Gonadotropin-Releasing Factor Deficiency
GnRH deficiency may arise due to genetic mutations, developmental anomalies, or acquired conditions. Common causes include:
- Kallmann Syndrome: A genetic condition involving delayed puberty and anosmia (loss of smell).
- Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (IHH): A non-genetic form of GnRH deficiency.
- Pituitary or Hypothalamic Damage: Resulting from tumors, trauma, or radiation therapy.
Symptoms of Gonadotropin-Releasing Factor Deficiency
Symptoms vary by age and gender but may include:
- In Males: Delayed puberty, small testes, reduced muscle mass, and infertility.
- In Females: Lack of menstruation (amenorrhea), minimal breast development, and infertility.
- Both Genders: Decreased libido, fatigue, and osteoporosis risk.
Diagnosis of Gonadotropin-Releasing Factor Deficiency
Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests:
- Hormonal Blood Tests: To measure GnRH, LH, and FSH levels.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to evaluate the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations linked to GnRH deficiency.
Treatment Options for Gonadotropin-Releasing Factor Deficiency
Treatment focuses on hormone replacement and fertility restoration:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Testosterone in males and estrogen-progestin combinations in females.
- GnRH Pulsatile Therapy: Administered via pump for optimal hormonal balance.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): In vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Potential Complications
Untreated GnRH deficiency may result in:
- Infertility
- Osteoporosis
- Cardiovascular issues
- Psychological distress due to delayed puberty
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With proper diagnosis and treatment, most individuals with GnRH deficiency can lead normal, healthy lives. Continuous monitoring and hormone adjustments are crucial for maintaining hormonal balance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What triggers gonadotropin-releasing factor deficiency?
Genetic mutations, brain injuries, and hormonal imbalances can all contribute.
Is GnRH deficiency treatable?
Yes, hormone replacement therapy and fertility treatments are effective solutions.
Can individuals with GnRH deficiency have children?
With appropriate medical intervention, conception is often possible.
Does GnRH deficiency affect lifespan?
If treated effectively, life expectancy remains normal.
How is GnRH deficiency different from delayed puberty?
GnRH deficiency is a permanent hormonal disorder, whereas delayed puberty often resolves naturally.