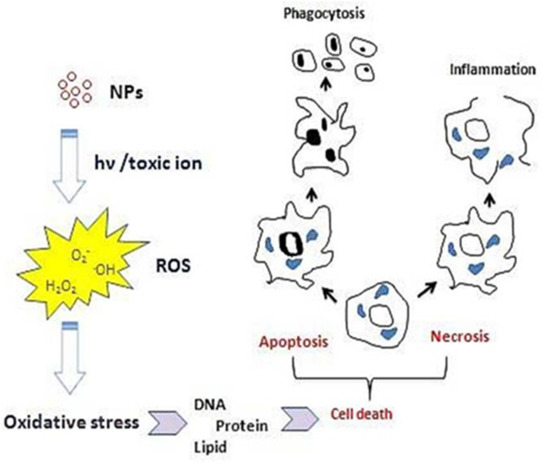
Gold toxicity, also known as gold poisoning, is a rare yet serious medical condition that occurs when excessive amounts of gold accumulate in the body. While gold is widely used in medical treatments and dental applications, prolonged exposure or excessive administration can lead to toxic effects.
What Causes Gold Toxicity?
Gold toxicity primarily occurs due to:
- Medical Treatments: Gold salts are sometimes prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions, posing a risk of toxicity with long-term use.
- Industrial Exposure: Individuals working in industries like mining, jewelry manufacturing, or electronics are at higher risk.
- Ingestion of Gold Particles: Certain traditional medicines or gold-infused supplements may contain harmful levels of gold.
Symptoms of Gold Toxicity
Gold toxicity can manifest through a range of symptoms, which may vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Dermatitis: Redness, itching, and skin irritation.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Proteinuria (presence of protein in urine) and nephrotic syndrome.
- Hematological Issues: Bone marrow suppression leading to anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia.
- Neurological Effects: Peripheral neuropathy, headaches, and confusion.
- Mucosal and Oral Lesions: Stomatitis (oral inflammation) is a common indicator of gold toxicity.
Diagnosis of Gold Toxicity
Accurate diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Diagnostic steps include:
- Blood Tests: Elevated gold levels in blood samples.
- Urine Analysis: High gold concentration in urine.
- Clinical History: Reviewing patient exposure to gold-based medications or work environments.
Treatment for Gold Toxicity
Effective management of gold toxicity involves the following steps:
- Discontinuation of Gold Therapy: Immediate cessation of gold-based treatments.
- Chelation Therapy: Administering agents like dimercaprol to bind and remove gold from the body.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms such as renal impairment or anemia through appropriate treatments.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular assessment to ensure the patient’s recovery and avoid long-term complications.
Prevention of Gold Toxicity
Preventive measures are essential to reduce the risk of gold toxicity:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients undergoing gold-based therapies should undergo frequent health checks.
- Proper Industrial Safety: Workers handling gold should wear protective equipment to minimize exposure.
- Awareness in Alternative Medicine: Educating patients about the risks of consuming gold-infused traditional medicines.
Gold toxicity is a rare yet severe condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and preventive strategies, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with gold exposure and ensure their well-being.